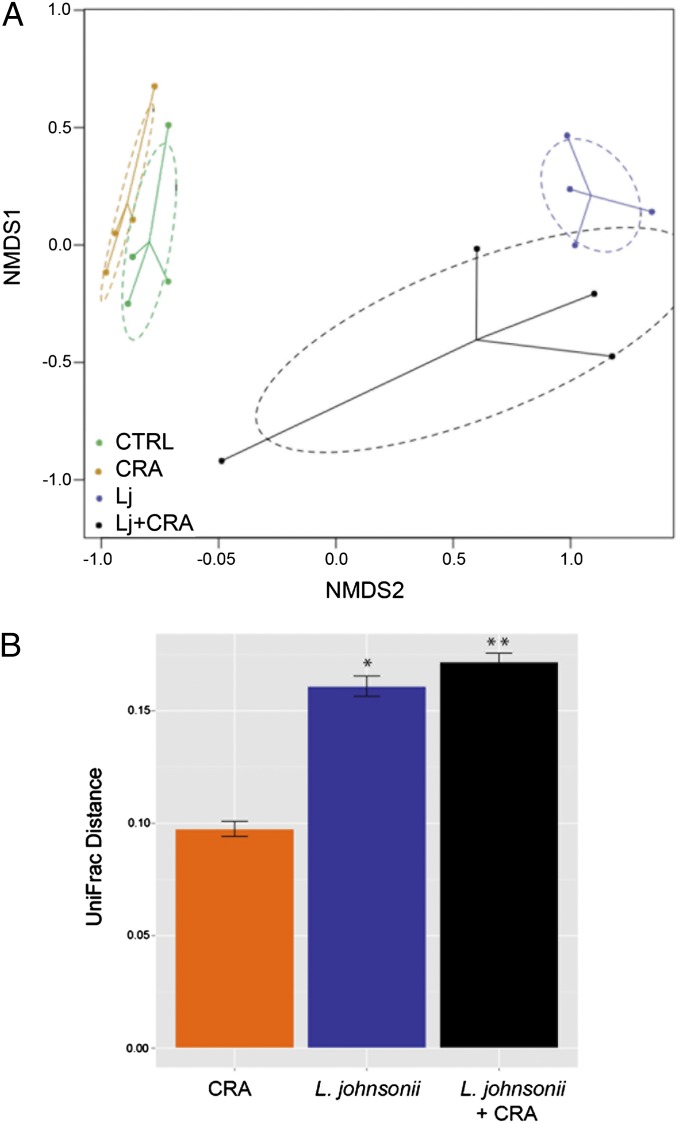
Fig. 5.
(A) L. johnsonii-supplemented animals that exhibit airway protection exhibit altered cecal microbiome composition. Nonmetric dimensional scaling based on a UniFrac distance matrix reveals that microbial communities of mice supplemented with L. johnsonii are compositionally and phylogenetically distinct from unsupplemented animals. Ellipses constructed around each treatment group indicate the 95% confidence intervals. (B) Compared with unsupplemented control animals, communities supplemented with L. johnsonii or L. johnsonii followed by CRA exposure exhibit the greatest phylogenetic distance (*P < 0.0005, **P < 0.0001, respectively).