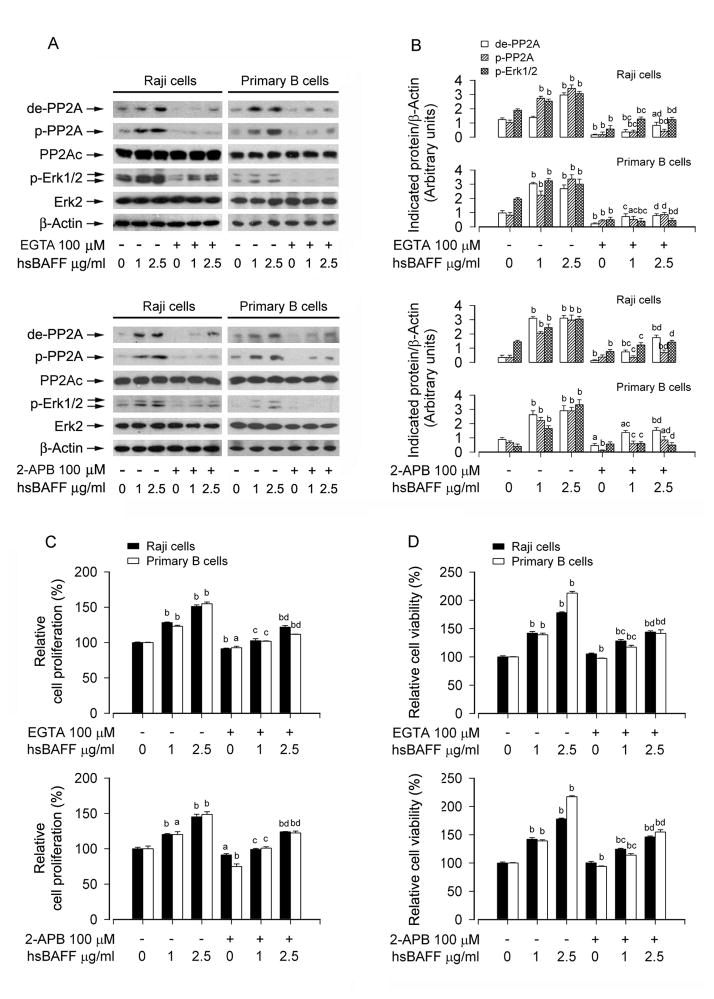
Fig. 7.
EGTA or 2-APB attenuates hsBAFF-induced inhibition of PP2A and activation of Erk1/2 as well as cell proliferation/viability in B cells. Raji cells and purified mouse splenic B lymphocytes were treated with 0, 1, 2.5 μg/mL hsBAFF for 12 h (for Western blotting) or 48 h (for cell proliferation/viability assay) following pretreatment with/without 100 μM EGTA or 100 μM 2-APB for 1 h. Total cell lysates were subjected to Western blotting using indicated antibodies (A). The blots were probed for β-actin as a loading control. Similar results were observed in at least three independent experiments. The cell proliferation was evaluated by cell counting (C) and the cell viability was determined by the MTS assay (D). (A) hsBAFF-induced inhibition of PP2A and activation of Erk1/2 were strongly blocked by EGTA and 2-APB, respectively. (B) Blots for de-PP2A, p-PP2A, and p-Erk1/2 were semi-quantified using NIH image J. (C and D) EGTA or 2-APB markedly inhibited the basal or hsBAFF-stimulated cell proliferation and viability. Results are presented as mean ± SE (n = 3–6). aP <0.05, bP <0.01, difference vs 0 μg/mL hsBAFF group; cP<0.01, difference vs 1 μg/mL hsBAFF group; dP<0.01, difference vs 2.5 μg/mL hsBAFF group.