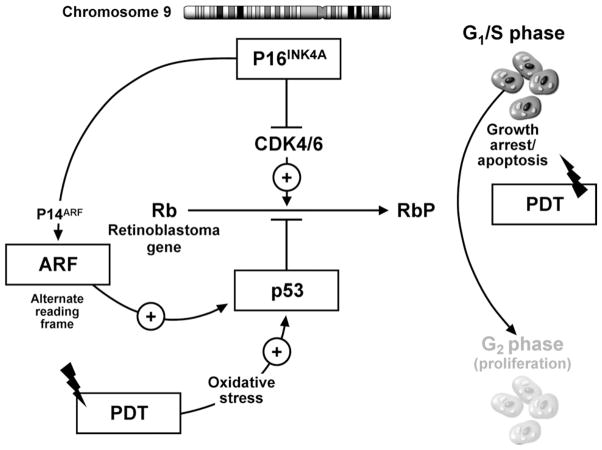
Figure 4.
Putative model of the influence of cell-cycle check point genes on PDT-induced cellular apoptosis. The p16 locus on chromosome 9 can transcribe 2 proteins: (1) P16INK4 protein, which inhibits CDK4 and CDK 6, leading to the inhibition of phosphorylation of the retinoblastoma gene product (Rb), causing inhibition of cell-cycle progression and growth arrest, and (2) p14ARF, which inhibits the degradation of p53 protein by MDM2, thereby potentiating the P53-mediated inhibition of cell-cycle progression and causing cell-cycle arrest. PDT causes oxidative stress, which can activate cellular apoptosis mechanisms by P53-dependent and -independent mechanisms. In the presence of intact p16 (p14 ARF) and p53 function, PDT can induce cell injury by apoptosis. Loss of p16 and p53 function allows the progression of cells to the G2 phase of the cell cycle, leading to cell proliferation. This may provide cells with a survival advantage, leading to decreased response to PDT.