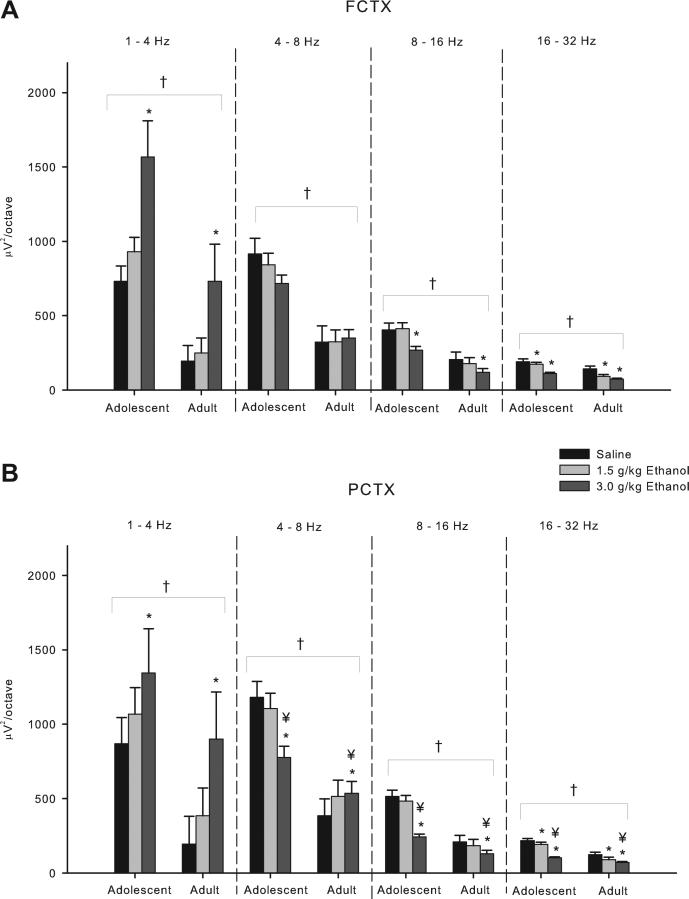
Fig. 1.
Acute effects of ethanol on electroencephalogram (EEG) power in adolescent and adult rats following acute saline/ethanol challenge. (A) Frontal cortex EEG in adolescent rats has greater power across all frequency bands compared to adults. Further post hoc analyses show a 3.0 g/kg ethanol dose effect in the delta (1–4 Hz), midrange (8–16 Hz), and beta (16–32 Hz) bands as well as a 1.5 g/kg dose effect in the beta band. (B) Power in the parietal cortex was found to be higher in adolescents than in adults across all frequency bands. Post hoc analyses show a 3.0 g/kg dose effect in all frequency bands, and in the beta band at the 1.5 g/kg dose. Age × ethanol interactions were seen at the 3.0 g/kg dose in the theta (4–8 Hz), midrange, and beta frequency bands. * indicates p < 0.05 ethanol effect. † indicates p < 0.05 age effect. ¥ indicates p < 0.05 age × ethanol interaction. Error bars = SEM.