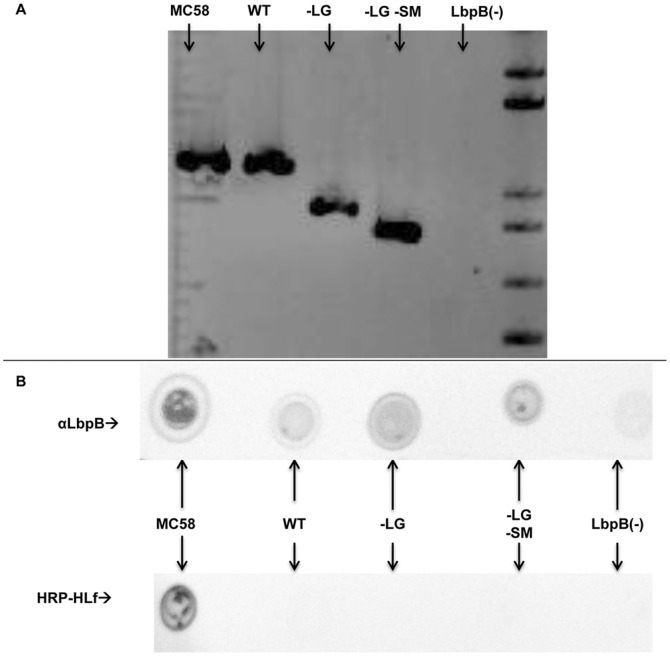
Figure 4. Characterization of the LbpB mutants.
Panel A: Colony PCR was used to amplify the DNA region encoding the LbpB C-Lobe from wild-type and mutant N. meningitidis strains. PCR products were run on a 1.4% agarose gel with a 1KB plus DNA ladder (L) and visualized using ethidium bromide. Panel B: Solid phase binding assays were performed using MC58 LbpB specific antibodies (top) or HRP conjugated human lactoferrin (bottom). Antibodies were used to confirm the expression of LbpB at the cell surface, while human lactoferrin was used to evaluate LbpA expression. All strains except MC58 have an antibiotic resistance cassette inserted in front of the lbpA gene. In both panels MC58 is the parental wildtype N. meningitidis strain and WT indicates the gentamicin resistant strain that expresses the wild-type MC58 LbpB (N368). -LG indicates the strain expressing LbpB lacking the large negatively charged region (N365), and -LG –SM indicates the strain expressing LbpB that lack both negatively charged region (N366). LbpB(−) indicates the chloramphenicol resistant mutant lacking the lbpB gene (N364).