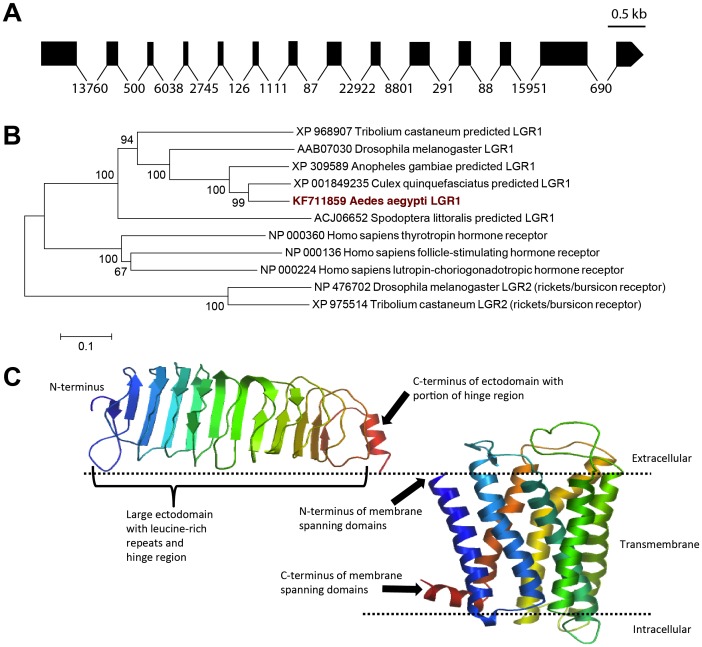
Figure 4. Gene model of open reading frame-spanning exons, phylogenetic analysis and structural modeling of the Aedes aegypti LGR1 receptor.
In (A), legend bar denotes length of 0.5 kb and is proportional only for exons (shaded boxes). Introns (denoted by lines) have been standardized and are not proportional to size in order to optimize illustration of exon lengths. Numbers below lines adjoining exons denote predicted intron sizes based on A. aegypti genomic data. In (B), the evolutionary relationship was inferred using neighbor-joining method and statistical support was tested by 1000 bootstrap iterations where numbers adjacent to the branches denote the percentage of replicate trees in which the associated taxa clustered together. The tree is drawn to scale, with branch lengths indicative of the number of amino acid substitutions per site. In (C), a schematic representation of the major structural features of the AedaeLGR1, which includes the large ectodomain (containing leucine-rich repeats and hinge region) and seven transmembrane domains (see Results section). Note that portions of the protein lacking major predicted structural features are omitted from this schematic model. Given the low overall conservation within the hinge region of the ectodomain, the model of this feature is truncated and includes only the N-terminal portion of the hinge region.