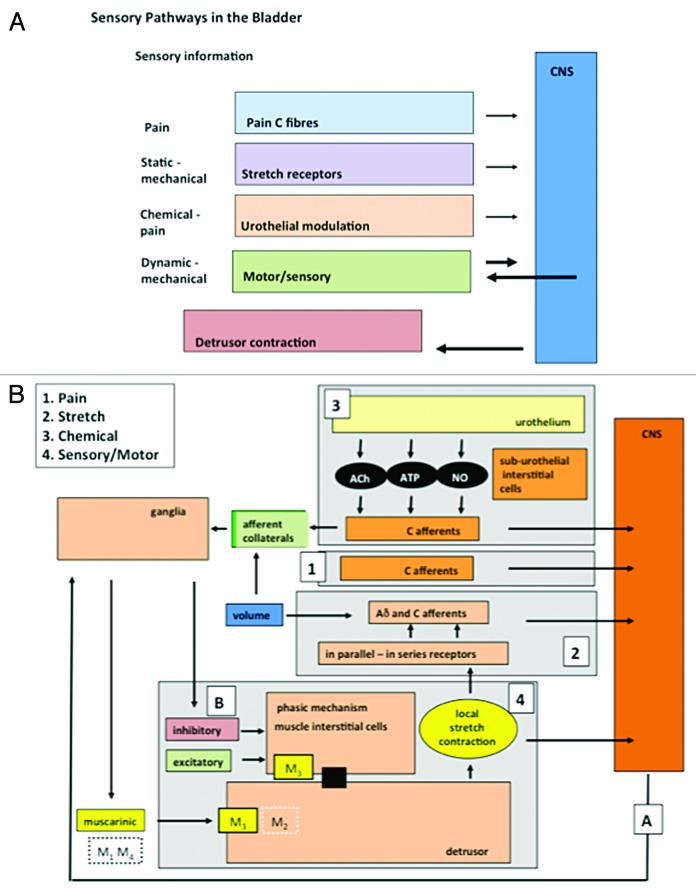
Figure 1.
The components of afferent noise in the guinea pig. (A) Illustrates the broad elements of the afferent systems associated with the bladder: components of afferent noise. Four are identified: pain, mechano-sensory, urothelial and motor-sensory. Each sends afferent information to the CNS but only the motor-sensory system has the potential for an output from the CNS and inputs from peripheral afferent fibers. (B) Illustrates in more detail some of the component parts of the systems making up afferent noise. The afferent out flow to the CNS can again be seen for each system: 1, pain; 2, mechano-sensitive (stretch); 3, urothelial; 4, motor-sensory. For the motor-sensory system, part of the complex regulatory systems involved in the regulation of motor activity may be occurring via the intra-mural ganglia and local neural circuits within the bladder wall. Reprinted from reference 43 with permission.