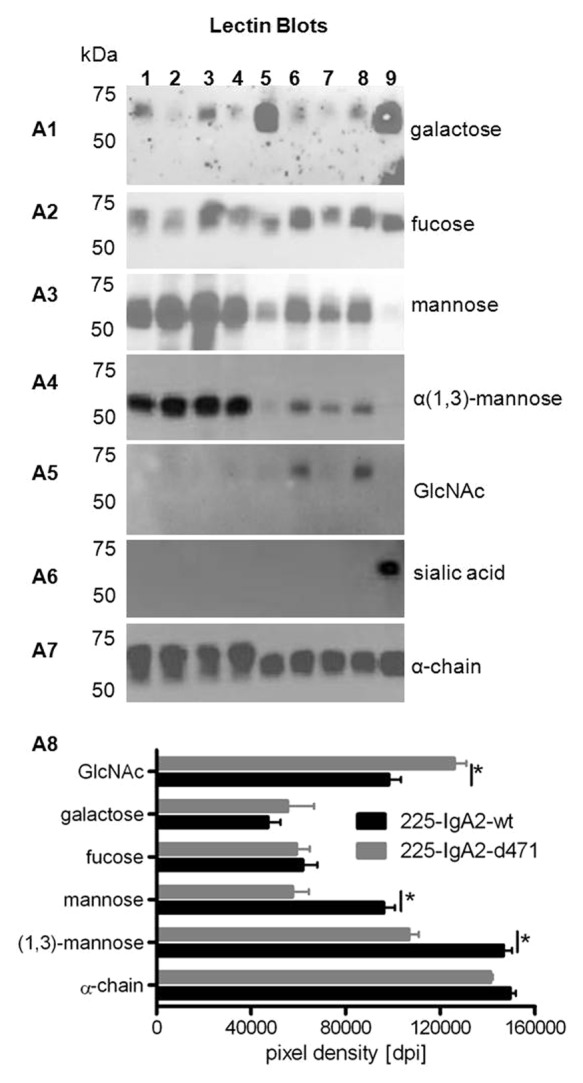
Figure 4. Glycosylation of wild type and d471-mutated IgA2 antibodies. Single clones producing 225-IgA2-wt and –d471 were cultured in tissue culture flasks (TCF), and glycosylation of affinity-purified antibodies was analyzed using lectin blots. Different sugar moieties were detected using biotinylated lectins specific for terminal galactosylation (A1), α(1,6)-linked fucosylation (A2), α-linked mannosylation (A3), α(1,3)-linked mannosylation (A4), N-acetylglucosamine (A5), terminal sialic acid (A6), and human α-chain as loading control (A7). Lanes: 1. 225-IgA2-wt (CL1000 produced), 2. 225-IgA2-wt clone 1, 3. 225-IgA2-wt clone 2, 4. 225-IgA2-wt clone 3, 5. 225-IgA2-d471 (CL1000 produced), 6. 225-IgA2-d471 clone 1, 7. 225-IgA2-wt clone 2, 8. 225-IgA2-wt clone 3, 9. control IgA2. (A8) To evaluate whether that glycosylation of wild type and mutant IgA2 antibodies was different, lectin blots were analyzed densitometrically using ImageJ software. Results are presented as “pixel density (dots per inch [dpi])” and significant differences between wild type and mutant IgA2 glycosylation are indicated by * (P ≤ 0.001).
