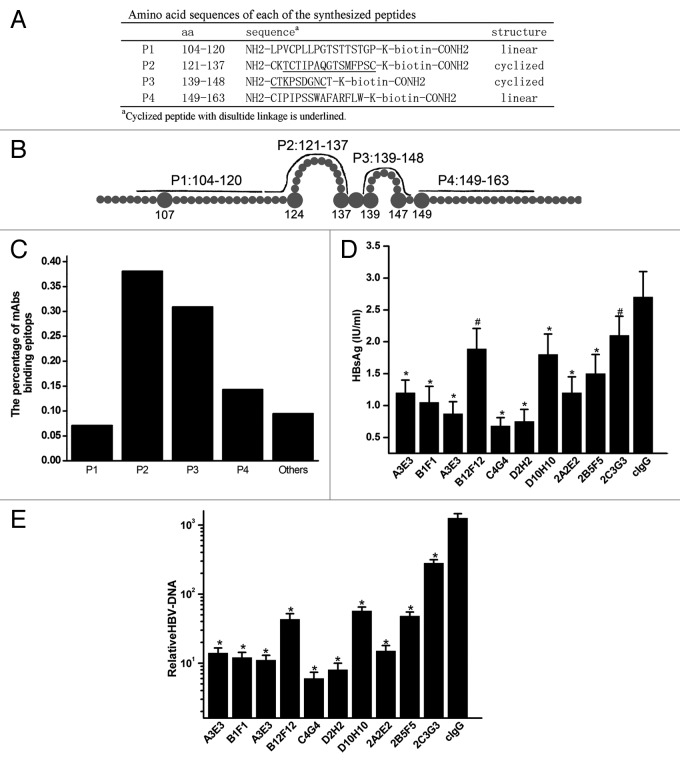
Figure 2. Characterization of anti-HBsAg antibodies. (A) Amino acid sequences of the synthesized peptides. The bold lines represent lined (P1 and P4) and cyclized synthesized peptides (P2 and P3) on conformational structure of the extracellular domain of HBsAg. (B) Schematic representation of synthesized peptides covering the extracellular domain of HBsAg. (C) Proportion of mAbs binding to synthesized peptides by ELISA. (D) Quantification of HBsAg levels in the supernatant of HepaRG cells and HBV-DNA in the cells at 7 d after infection with HBV pretreated with antibodies. (E) Quantification of HBV-DNA in HepaRG cells at 7 d after infection with HBV pretreated with mAbs. Results were shown as mean ± SD of three independent experiments. *P < 0.05; #P > 0.05.

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.