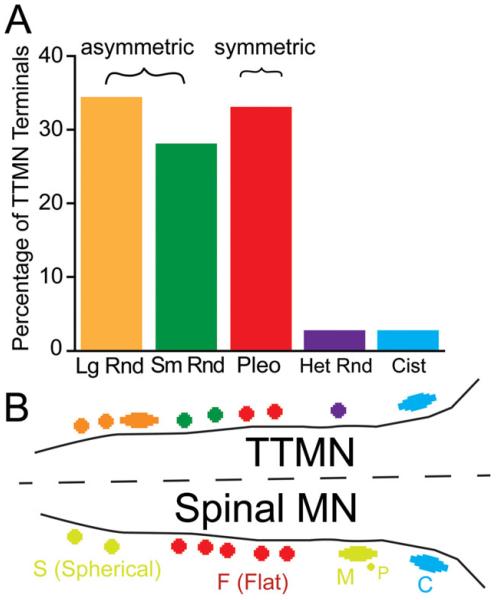
Fig. 8.
A: Percentages of each type of synaptic terminal on all six TTMNs examined in the electron microscope. Lg Rnd-Large Round; Sm Rnd-Small Round; Pleo-Pleomorphic; Het Rnd-Heterogeneous Round; Cist-Cistern. Brackets indicate the synaptic types that are asymmetric (having a prominent postsynaptic density) and those that are symmetric (having minimal postsynaptic density). B: Schematic of synaptic terminal types found on TTMNs, and comparison to types found on spinal α-motoneurons (after Conradi et al., 1979). Apparent correspondences are indicated with similar colors. S: spherical-vesicle synaptic terminals; M: large terminals containing spherical vesicles that receive input from other, presynaptic (P) terminals, or which have a synaptic complex with six or more “Taxi” bodies; F: flattened-vesicle synaptic terminals; C: cistern synaptic terminals.