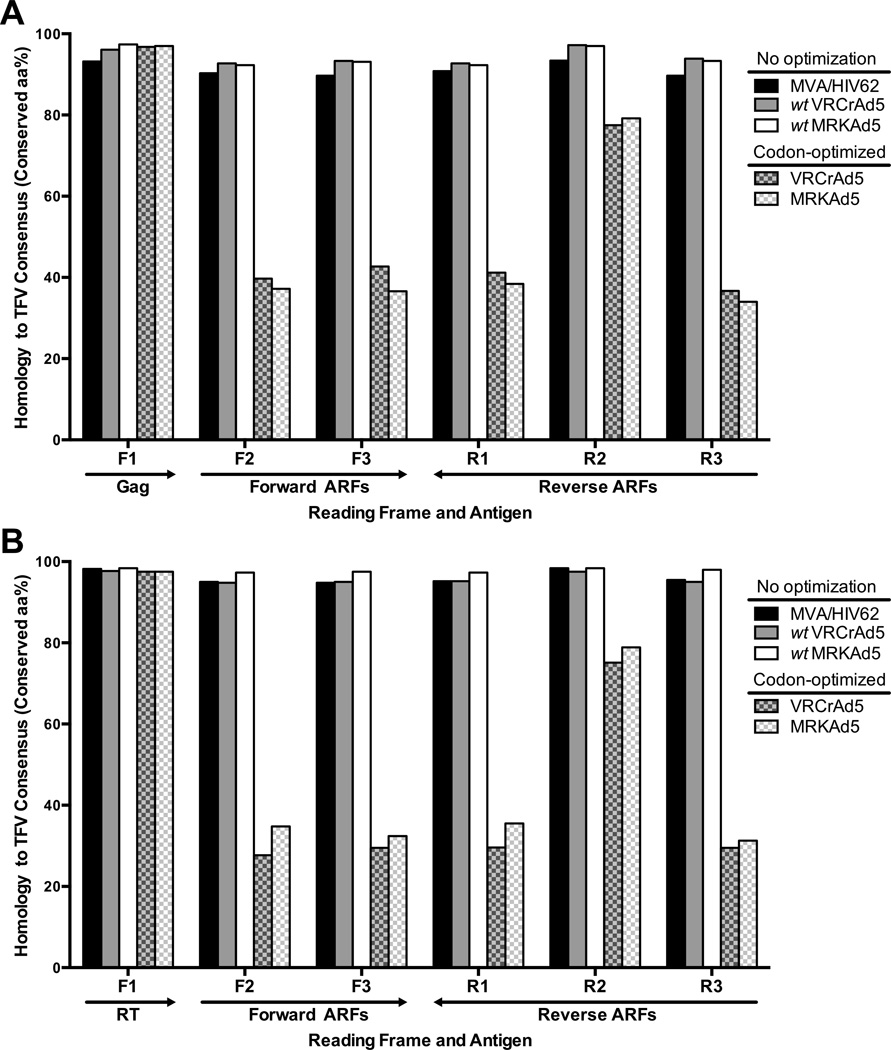
Figure 1. Codon optimization significantly alters natural HIV-1 ARFs.
The homology of amino acid sequences is plotted as the percent of residues that were conserved with respect to a reference, the translated TFV consensus sequence, for 1 noncodon-optimized insert (MVA/HIV62; black), 2 codon-optimized inserts (VRCrAd5, MRKAd5; grey and white pattern, respectively), and the 2 wild type sequences from which the codon-optimized insert were designed (wtVRCrAd5, wtMRKAd5; grey and white). Amino acid identities were compared for all reading frames of the gag (A) and RT (B) regions.