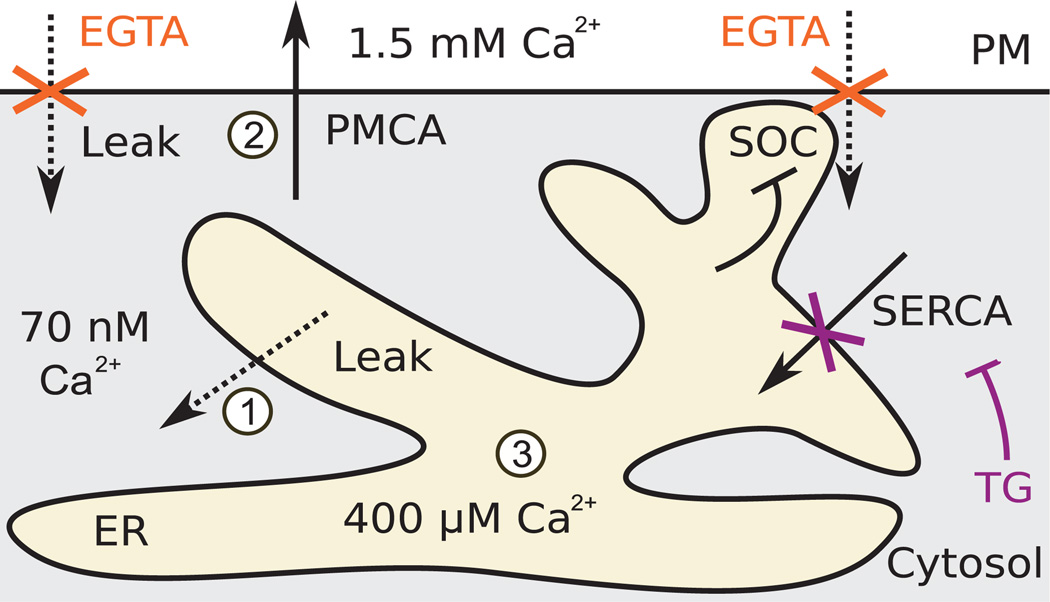
Fig. 1. Schematic of the core Ca2+ regulatory system.
PM Ca2+ pump PMCA maintains a large gradient of Ca2+ across the PM. Ca2+ pump SERCA in the ER membrane fills an ER Ca2+ store that is used in rapid signaling events. Both pump proteins maintain these gradients against the effects of leak through regulated and constitutively active Ca2+ channels. Depletion of the ER Ca2+ store triggers influx of Ca2+ from the outside in a process termed SOC, which is inhibited by ER Ca2+. Our experimental approach combined thapsigargin (TG) to block SERCA with EGTA to chelate external Ca2+, thus blocking entry of Ca2+ from the outside. Dashed arrows indicate passive, but possibly regulated, leak. Solid arrows indicate ATP (adenosine 5′-triphosphate)–driven pump activities. Numbers in white circles reference model terms in Fig. 2D.