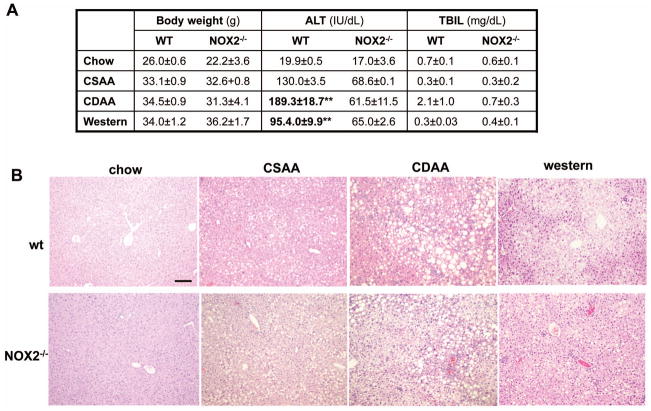
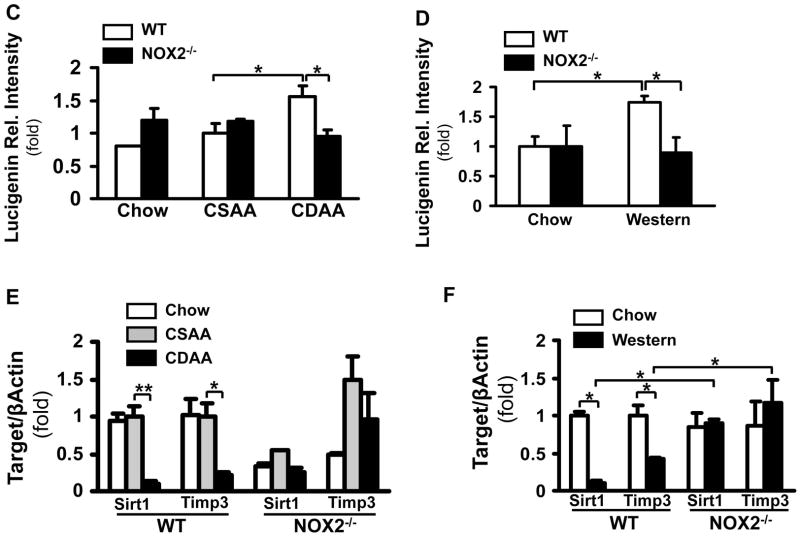
Figure 4. NOX2-dependent ROS production is increased in two diet models of NASH and is involved in the regulation of Sirt1 and Timp3.
WT and NOX2−/− mice were fed with the chow, CSAA, CDAA or western diet. Compared to the wt mice on the chow or CSAA diet, the wt CDAA and western diet-fed mice displayed an increase in weight; a significant increase of serum ALT (**p<0.01, N=6) and in the CDAA mice in total bilirubin. In the NOX2−/− mice there was no significant increase in ALT or bilirubin. (A). H&E staining showed that the wt and NOX2−/− mice on the CDAA and western diets had increased steatosis (B). The lucigenin assay demonstrated significantly increased superoxide production in the wt mice on the CDAA and western diets compared to those on the chow and CSAA diets (*p<0.05, N=6). No increase was seen in the NOX2−/− mice (*p<0.05, N=6) (C, and D). SirT1 andTimp3 mRNA expression was assessed by real-time qPCR in the wt and NOX2−/− mice. SirT1 and Timp3 expression significantly decreased in the wt CDAA (E) and western diet (F) fed mice (**p<0.01 and *p<0.05, respectively, N=6). In contrast, in NOX2−/− mice Sirt1 andTimp3 expression remained unchanged.