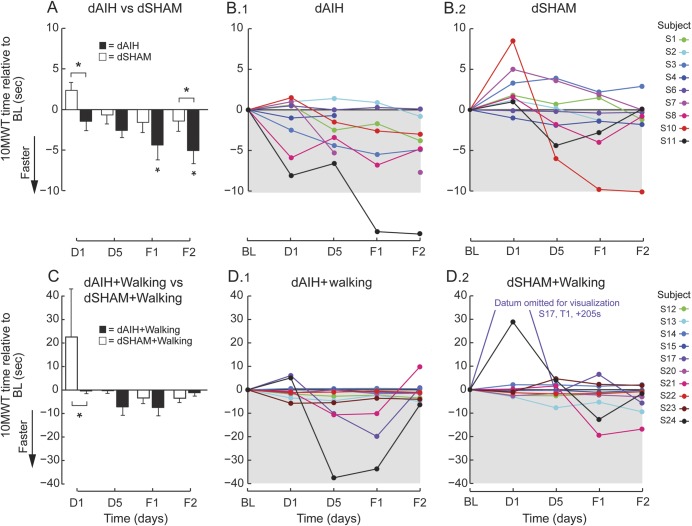
Figure 2. dAIH-induced increases in overground walking speed in persons with chronic incomplete spinal cord injury.
(A) Bars represent mean ± 1 standard error changes in 10-Meter Walk Test (10MWT) times (seconds) across all subjects at each time point for daily acute intermittent hypoxia (dAIH) (black) and daily normoxia (dSHAM) (white). Asterisks indicate significance relative to baseline (BL) (repeated-measures linear mixed model, p < 0.05) and brackets with asterisks indicate significant differences between interventions dAIH and dSHAM (repeated-measures linear mixed model, p < 0.05). (B) Subject changes in 10MWT times (seconds) relative to BL across days 1 (D1) and 5 (D5) and follow-ups 1 (F1) and 2 (F2) during dAIH intervention (B.1) and during dSHAM intervention (B.2). Decreases in time represent increases in walking speed. (C) Same mean comparisons as in panel A for dAIH + walking (black) and dSHAM + walking (white). (D) Same subject trends as in panel B for dAIH + walking (D.1) and dSHAM + walking (D.2).