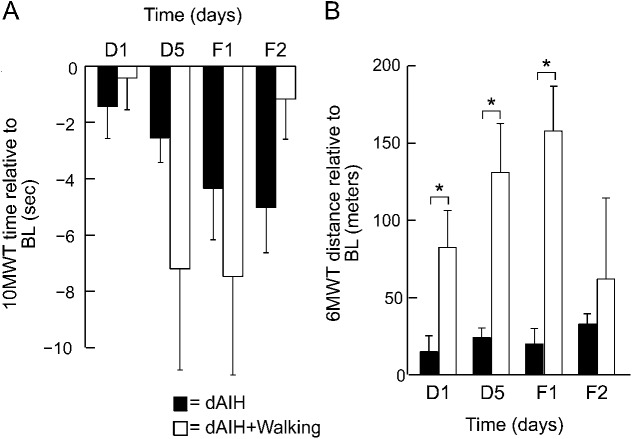
Figure 4. dAIH with daily overground walking produces greater improvements in walking compared with dAIH alone.
(A) Bars represent mean ± 1 standard error changes in 10-Meter Walk Test (10MWT) times (seconds) across all subjects at days 1 (D1) and 5 (D5) and follow-ups 1 (F1) and 2 (F2) for daily acute intermittent hypoxia (dAIH) (black) or the combinatorial intervention of dAIH with daily overground walking (white). (B) Same trends as in panel A for mean ± 1 standard error changes in 6-Minute Walk Test (6MWT) distances (meters). Brackets with asterisks indicate significant differences between interventions dAIH and dAIH + walking (repeated-measures linear mixed model, p < 0.05). BL = baseline.