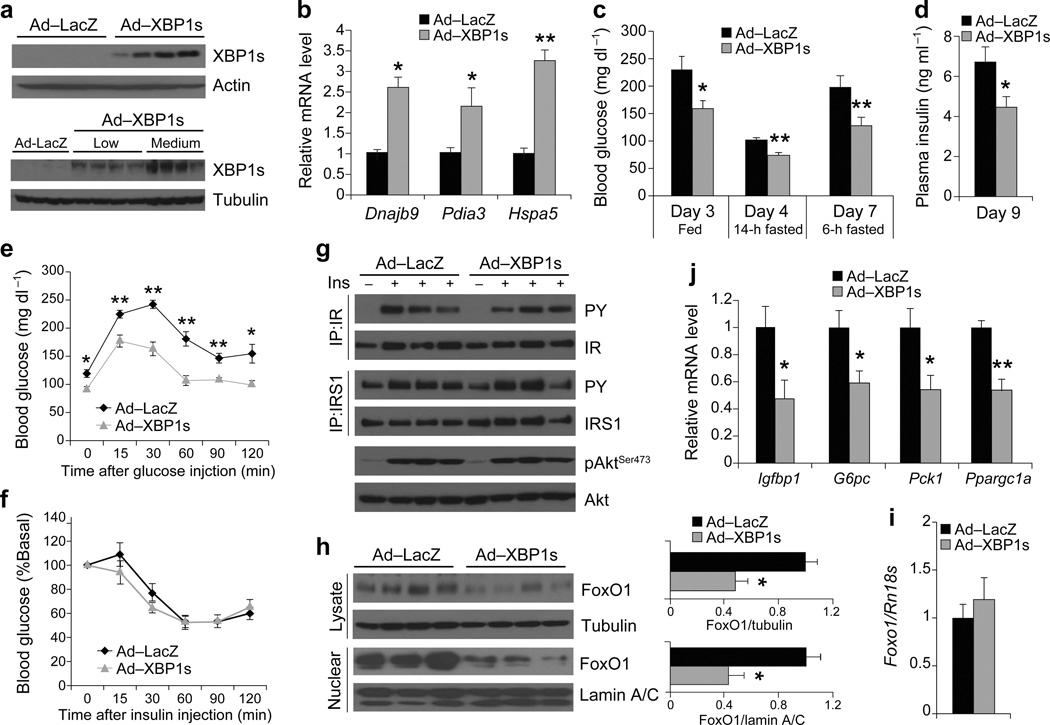
Figure 2.
Medium-level expression of XBP1s in ob/ob mice improves glucose homeostasis without altering the insulin receptor signaling. Seven-week-old, male, ob/ob mice were injected with Ad-LacZ (n = 6) or Ad-XBP1s (n = 6) (4 × 107 PFU g−1) through tail vein. (a) XBP1s protein levels in the liver of ob/ob mice injected with low or medium dose of adenovirus. (b) Relative mRNA levels of XBP1s target genes, Dnajb9, Pida3 and Hspa5 in the liver of Ad-LacZ- or Ad-XBP1s-injected mice. (c) Blood glucose levels in fed, 6h and 14h fasting on indicated days after injections. (d) Plasma insulin levels on day 9, (e) GTT on day 5, and (f) ITT on day 7 after the injections. (g) IR and IRS1 tyrosine and AktSer473 phosphorylations with or without insulin stimulation in the liver on post-injection day 9. (h) Total and nuclear levels of FoxO1 protein in the liver of Ad-LacZ- or Ad-XBP1s-injected ob/ob mice. Graph depicts total FoxO1/tubulin and nuclear FoxO1/lamin A/C ratios. Relative mRNA levels of (i) Foxo1, (j) Igfbp1, G6pc, Pck1, and Ppargc1a in the liver of adenovirus-injected mice. Experiments were repeated in five independent cohorts. Error bars are ± s.e.m.; P values were determined by Student’s t-test (* P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001).