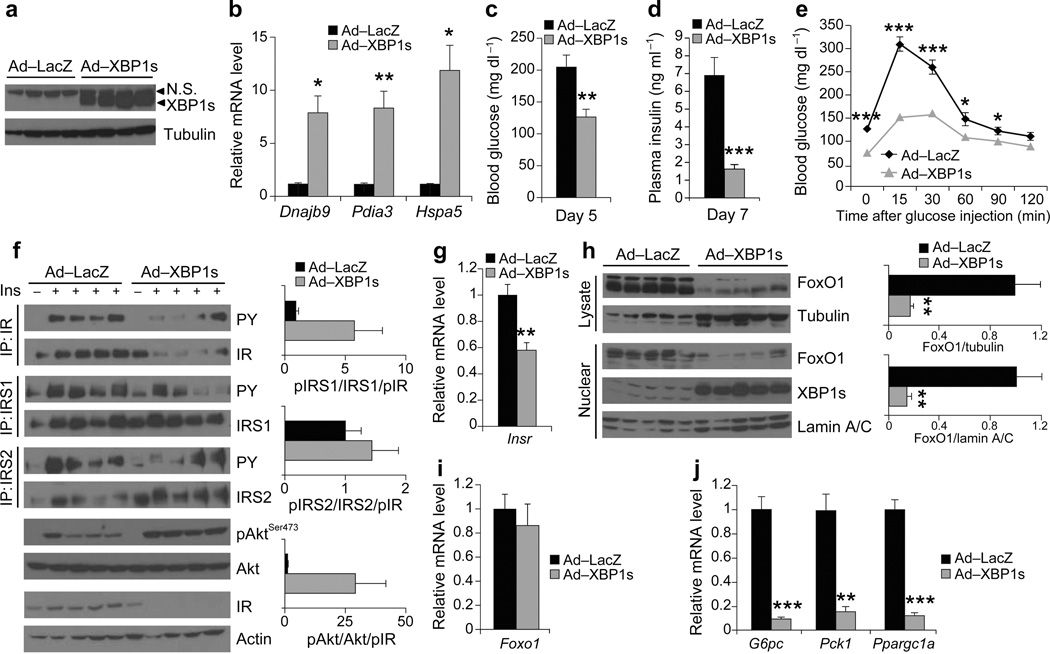
Figure 3.
High-level expression of XBP1s in the liver of ob/ob mice increases insulin sensitivity. Seven-week-old, male, ob/ob mice were injected with Ad-LacZ (n = 6) or Ad-XBP1s (n = 6) (1.8 × 108 PFU g−1) through tail vein. (a) XBP1s protein levels in the liver lysates on day 6 after injection. (b) Dnajb9, Pida3 and Hspa5 mRNA levels in the liver of Ad-LacZ- or Ad-XBP1s-injected mice. (c) Fed blood glucose levels on day 5, (d) plasma insulin levels on day 7, and (e) GTT on day 3 after the adenovirus injections. (f) In vivo insulin receptor signaling in the liver of Ad-LacZ- or Ad-XBP1s-injected ob/ob mice on post injection day 6. Graphs depicts the (phospho/total)/pIR ratios. (g) Relative mRNA levels of Insr in the liver of adenovirus-injected mice on day 6 after injection. (h) Total and nuclear FoxO1 levels in the liver of Ad-LacZ- or Ad-XBP1s-injected ob/ob mice. Graph depicts total FoxO1/tubulin and nuclear FoxO1/lamin A/C ratios. Relative mRNA levels of (i) Foxo1 and (j) G6pc, Pck1, and Ppargc1a in the liver of Ad-LacZ- or Ad-XBP1s-injected ob/ob mice. Experiments were repeated in three independent cohorts. N.S: non-specific. Error bars are ± s.e.m.; P values were determined by Student’s t-test (* P < 0.05, ** P < 0.01, *** P < 0.001).