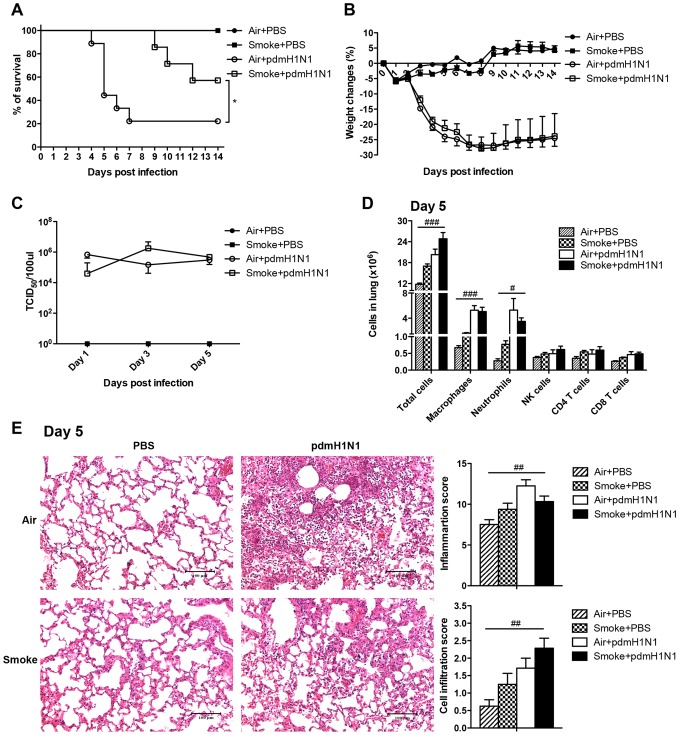
Figure 2. Cigarette smoke exposure decreased the severity of pdmH1N1 infection in mice.
The mice were exposed to room air or cigarette smoke for 21 days and then infected with pdmH1N1 virus. A) Survival curve of mice infected with pdmH1N1 virus. There were 6-9 mice per group. Data are representative of three independent experiments. B) Body weight changes of mice infected with pdmH1N1 virus. There were 6–9 mice per group. Data are representative of three independent experiments. C) Lung virus titers of pdmH1N1 infected mice. There were 4–10 mice per group. Data are representative of two independent experiments. D) Absolute number of lung cells on day 5 of pdmH1N1 infection. Macrophages (CD11b+, F4/80+), neutrophils (CD11b+, Ly-6G+), NK cells (CD3−, NK1.1+), CD4+ T cells (CD3+, CD4+) and CD8+ T cells (CD3+, CD8a+). There were 4–5 mice per group. E) Histopathological analysis of pulmonary tissues collected on day 5 of pdmH1N1 infection. Results are representative pictures (200X) of hematoxylin and eosin stained pulmonary tissues. Scale bar: 100 µm. Inflammation score and cell infiltration score were evaluated by a board-certified pathologist. There were 4–8 mice per group. Data are representative of two independent experiments. Results represent mean ± SEM. *p<0.05 was determined by Log-rank (Mantel-Cox) test; # p<0.05, ## p<0.01; ### p<0.001 were tested by ANOVA of four groups.