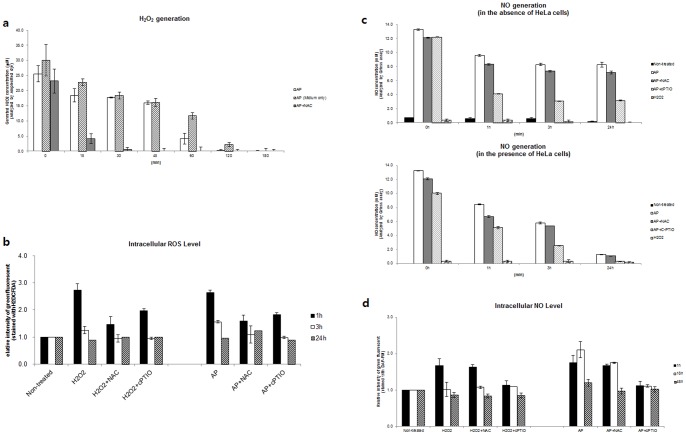
Figure 3. Treatment of antioxidants reduced level of extra- and intracellular ROS/RNS generated by air plasma.
(a) Levels of extracellular H2O2 were determined in culture or non-culture (Medium only) supernatants with air plasma treatment in the presence (AP + NAC) or absence (AP) of the antioxidant NAC (n = 5). NAC was added 1h prior to plasma treatment. The culture supernatant was harvested at the indicated times following air plasma treatment. AP 0 (min) indicates supernatant harvested immediately after plasma treatment. (b) Generation of ROS including H2O2, OH−, and •O2 in the intracellular matrix following air plasma jet (AP) were determined using the ROS-sensitive probe H2DCFDA (n = 5). Cells were pretreated with the antioxidants NAC or cPTIO for 1h and then exposed to air plasma (AP+NAC or AP+cPTIO) or H2O2 (H2O2+NAC or H2O2+cPTIO). At indicated times following air plasma treatment, cells were harvested. The fluorescence of untreated cells (Non-treated) was arbitrarily set to 1. (c) Levels of extracellular NO were determined in non-culture (in the absence of HeLa cells, upper) and culture (in the presence of HeLa cells, bottom) supernatants at the indicated times after air plasma jet exposure by the Griess assay (n = 10). Medium in the presence or absence of HeLa cells was pretreated with NAC or cPTIO for 1h prior to exposure to plasma or H2O2. (d) Levels of intracellular NO were evaluated using DAF-FM. Data are shown as the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 10).