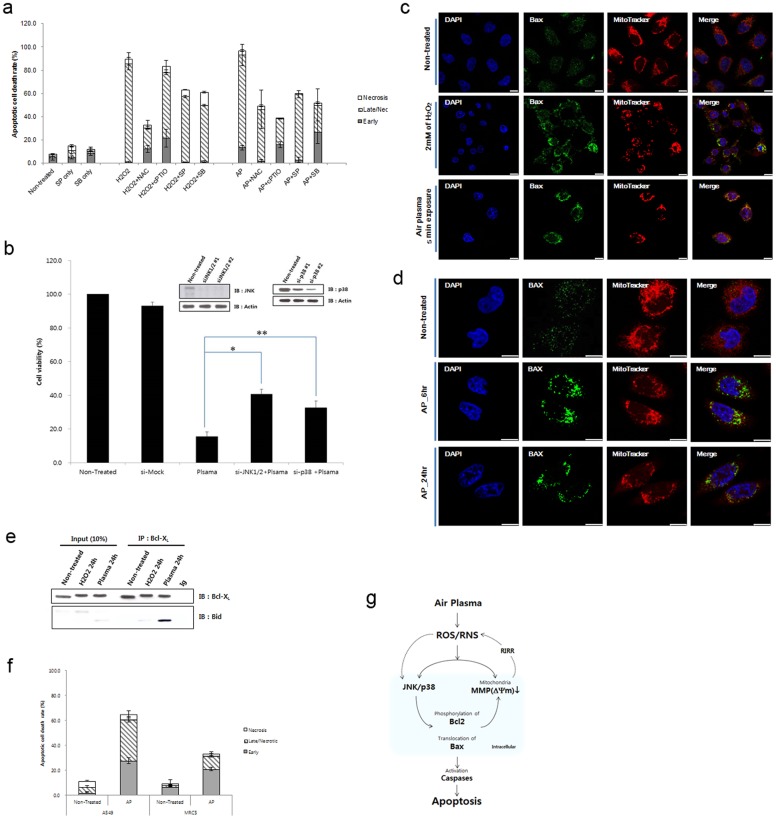
Figure 6. Air plasma induces cell death by activation of JNK and p38 via generating ROS and RNS.
(a) Antioxdizing agents (NAC and cPTIO) or kinase inhibitors (SP600125 and SB203580) partially rescued plasma-induced cell death. Data are shown as the mean ± S.E.M. (n = 10). (b) Plasma-induced cell death was partially abrogated in JNK1/2 (siJNK1/2) or p38 (sip38) knockdown cells. To monitor plasma-induced cell death, ATP-based cell viability assay was performed in the presence of control, JNK1/2, or p38 siRNA. Data are shown as the mean ± S.E.M. in triplicate from three independent experiment (n = 3). Cell viability of untreated HeLa cell population was arbitrarily set to 100%. Immunoblotting with anti-JNK and p38 antibodies was done to confirm knockdown. *p<0.01, **p<0.05. (c)–(d) Air plasma induced Bax translocation to the mitochondria. The plasma- or H2O2-treated cells were further incubated for 6–24 h. After 6–24 h incubation, cells were fixed by 3.7% formaldehyde. Bax (green) was stained anti-bax antibody and MitoTracker was used for staining of mitochondria (Red). Bax (green) and mitochondrial (red, MitoTracker) fluorescence were assessed, 6 h (d) and 24 h ((c) and (d)) after exposure to air plasma for 5 min by fluorescence confocal microscopy. Bax was diffusely distributed in untreated cells (non-treated). However, after treatment with plasma, Bax was localized to mitochondria, based on the overlap of the Bax and MitoTracker fluorescence images (Merge, yellow). DAPI was used for nuclear staining (blue). White bar was mean magnification of image (10 μM). (e) Bid formed a proapoptotic complex with Bcl-xL following plasma treatment. (f) Air plasma induced differential cell death in human lung adenocarcinoma A549 and normal lung fibroblast MRC5 cell lines. A549 and MRC5 cells were treated with air plasma jets and then incubated further for 24 h. After harvesting and staining cells with anti-annexin V-FITC and PI, cell death was evaluated by flow cytometry. The values represent the mean (s.e.m) from three independent experiments. (g) A proposed model for air plasma jet-induced apoptosis in HeLa cells through ROS/RNS production, trespassing on cells, activation of signal transduction pathways, and mitochondrial damage.