Fig. 2.
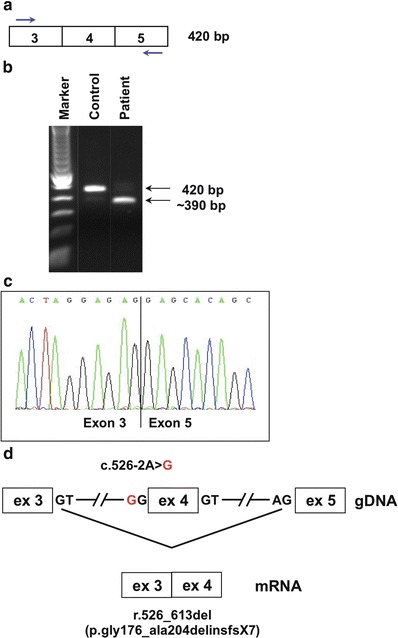
Aberrant splicing due to SLC17A5 mutation. Mutation analysis was performed on genomic DNA from whole blood by direct sequencing of all exons and exon/intron boundaries of SLC17A5 (NM_012434.4), according to standard protocols. For SLC17A5 mRNA studies, cDNA was prepared from cultured skin fibroblasts according to standard protocols: (a) Strategy for RT-PCR amplification of a region containing exon 4 (primer sequences and PCR protocol are available upon request). (b) The amplified product visualized on an agarose gel. The expected size of 420 bp is seen in an unaffected control, whereas in Patient 1, an additional band of approximately 350 bp was seen. (c) Direct sequence analysis of the ~350 bp fragment reveals an 88 bp deletion corresponding to exon 4. (d) A schematic overview of the gDNA with the acceptor splice site mutation c.526-2A>G. Disruption of the exon 4 splice acceptor site results in exon skipping, with exon 3 spliced directly onto exon 5 (r.526_613del). This is predicted to result in a frameshift and premature stop codon at the seventh downstream position (p.Gly176_Ala204delinsfs*7)
