Abstract
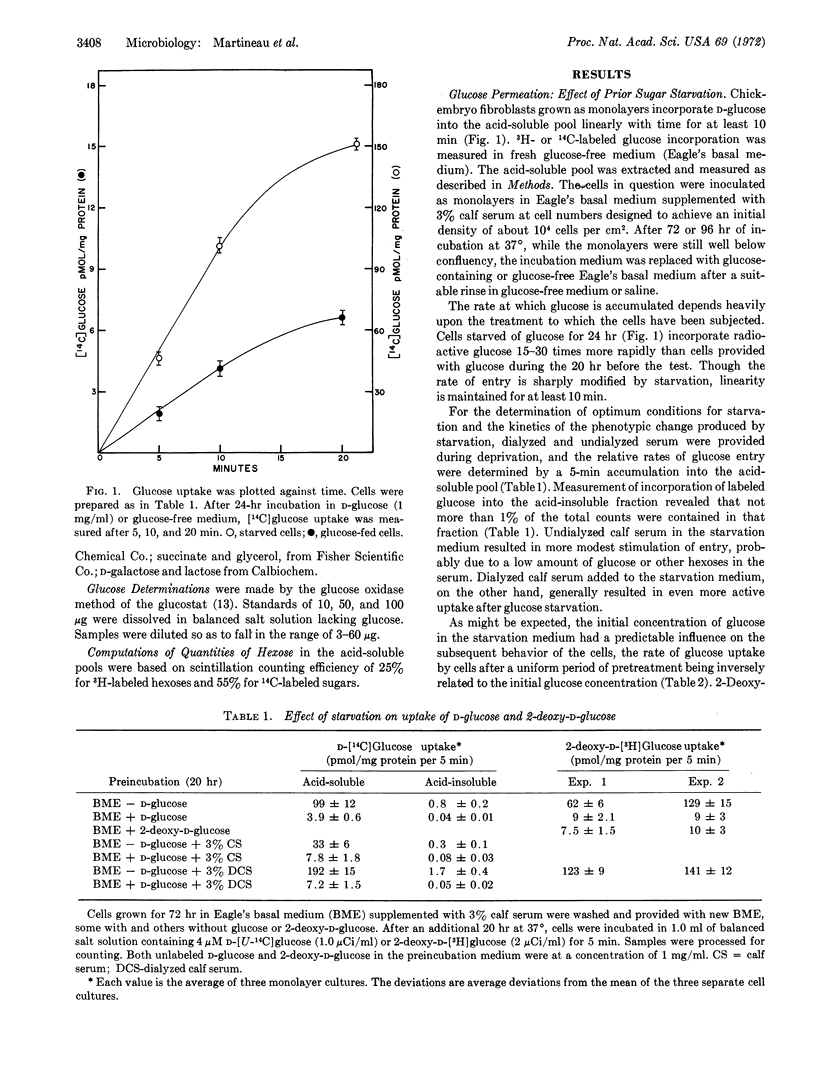
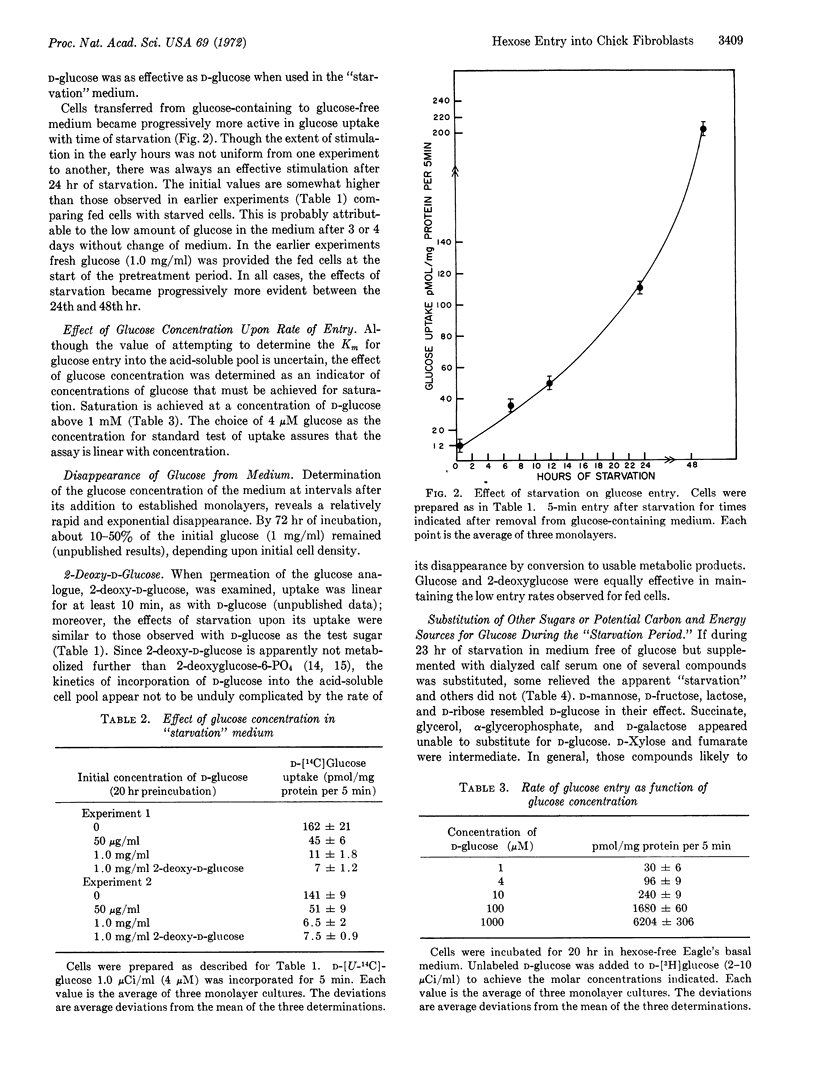
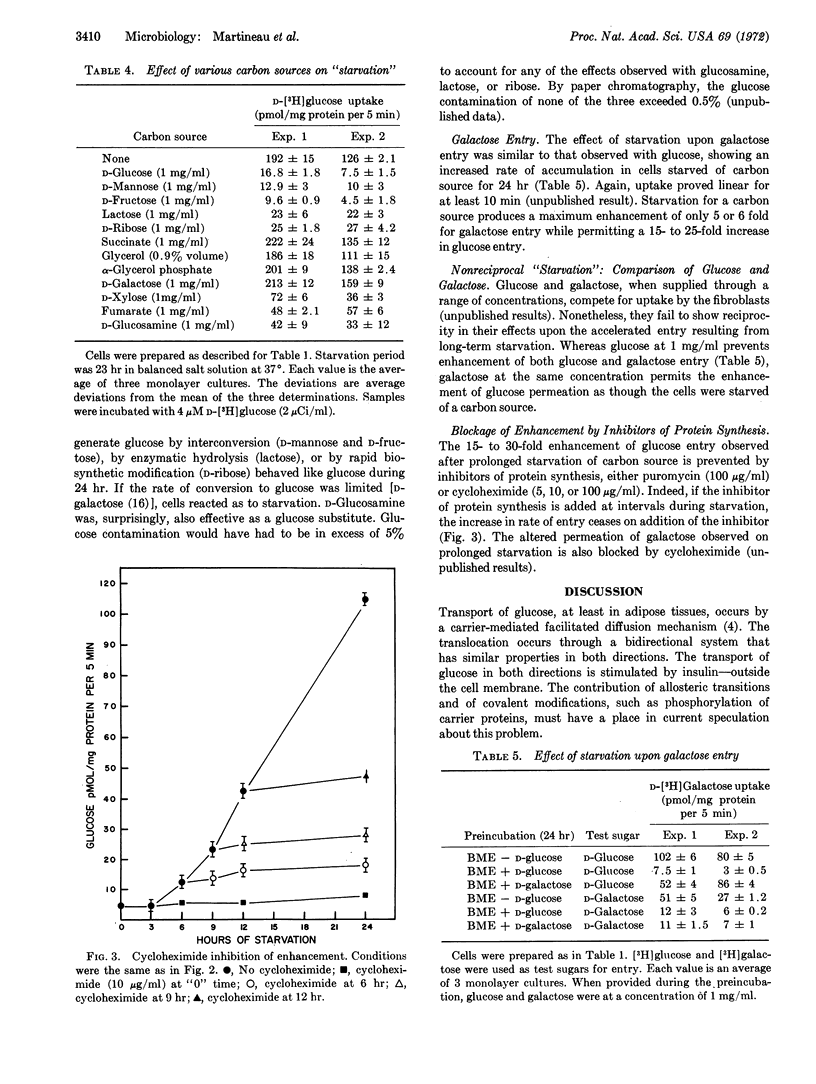
Glucose entry, as measured by 5-min uptake into the acid-soluble fraction, is enhanced 15-30 times by long-term (12-24 hr) hexose starvation of chick fibroblasts. The rate of galactose accumulation in the cells increases only 5 times under the same conditions of starvation. Several carbon and energy sources that were tested for their effect on this “derepression” can be classified as: (i) those resembling glucose in blocking the “stimulation,” (ii) those permitting full “derepression”; and (iii) those partially preventing the enhanced entry. Inhibitors of protein synthesis block enhancement under conditions otherwise conducive to it. We conclude that the glucose and galactose carrier systems are not identical, based largely on the asymmetric “repression” observed when glucose and galactose are compared as “repressors.”
Keywords: carrier-mediated diffusion, puromycin, cycloheximide
Full text
PDF

Selected References
These references are in PubMed. This may not be the complete list of references from this article.
- AMOS H., MOORE M. O. INFLUENCE OF BACTERIAL RIBONUCLEIC ACID ON ANIMAL CELLS IN CULTURE.I. STIMULATION OF PROTEIN SYNTHESIS. Exp Cell Res. 1963 Oct;32:1–13. doi: 10.1016/0014-4827(63)90063-6. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- CROFFORD O. B., RENOLD A. E. GLUCOSE UPTAKE BY INCUBATED RAT EPIDIDYMAL ADIPOSE TISSUE. CHARACTERISTICS OF THE GLUCOSE TRANSPORT SYSTEM AND ACTION OF INSULIN. J Biol Chem. 1965 Aug;240:3237–3244. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crane R. K., Forstner G., Eichholz A. Studies on the mechanism of the intestinal absorption of sugars. X. An effect of Na+ concentration on the apparent Michaelis constants for intestinal sugar transport, in vitro. Biochim Biophys Acta. 1965 Nov 29;109(2):467–477. doi: 10.1016/0926-6585(65)90172-x. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Crofford O. B. Countertransport of 3-O-methyl glucose in incubated rat epididymal adipose tissue. Am J Physiol. 1967 Jan;212(1):217–220. doi: 10.1152/ajplegacy.1967.212.1.217. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- EAGLE H. The specific amino acid requirements of a mammalian cell (strain L) in tissue culture. J Biol Chem. 1955 Jun;214(2):839–852. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Goldner A. M., Schultz S. G., Curran P. F. Sodium and sugar fluxes across the mucosal border of rabbit ileum. J Gen Physiol. 1969 Mar;53(3):362–383. doi: 10.1085/jgp.53.3.362. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- HUGGETT A. S., NIXON D. A. Use of glucose oxidase, peroxidase, and O-dianisidine in determination of blood and urinary glucose. Lancet. 1957 Aug 24;273(6991):368–370. doi: 10.1016/s0140-6736(57)92595-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Hatanaka M., Augl C., Gilden R. V. Evidence for a functional change in the plasma membrane of murine sarcoma virus-infected mouse embryo cells. Transport and transport-associated phosphorylation of 14C-2-deoxy-D-glucose. J Biol Chem. 1970 Feb 25;245(4):714–717. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Illiano G., Cuatrecasas P. Glucose transport in fat cell membranes. J Biol Chem. 1971 Apr 25;246(8):2472–2479. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Isselbacher K. J. Increased uptake of amino acids and 2-deoxy-D-glucose by virus-transformed cells in culture. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1972 Mar;69(3):585–589. doi: 10.1073/pnas.69.3.585. [DOI] [PMC free article] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- KIPNIS D. M., CORI C. F. Studies of tissue permeability. V. The penetration and phosphorylation of 2-deoxyglucose in the rat diaphragm. J Biol Chem. 1959 Jan;234(1):171–177. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Kaback H. R. Transport. Annu Rev Biochem. 1970;39:561–598. doi: 10.1146/annurev.bi.39.070170.003021. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- LOWRY O. H., ROSEBROUGH N. J., FARR A. L., RANDALL R. J. Protein measurement with the Folin phenol reagent. J Biol Chem. 1951 Nov;193(1):265–275. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Robinson E. A., Kalckar H. M., Troedsson H., Sanford K. Metabolic inhibition of mammalian uridine diphosphate galactose 4-epimerase in cell cultures and in tumor cells. J Biol Chem. 1966 Jun 25;241(12):2737–2745. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Rodbell M., Jones A. B., Chiappe de Cingolani G. E., Birnbaumer L. The actions of insulin and catabolic hormones on the plasma membrane of the fat cells. Recent Prog Horm Res. 1968;24:215–254. doi: 10.1016/b978-1-4831-9827-9.50011-3. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Schultz S. G., Curran P. F. Coupled transport of sodium and organic solutes. Physiol Rev. 1970 Oct;50(4):637–718. doi: 10.1152/physrev.1970.50.4.637. [DOI] [PubMed] [Google Scholar]
- Smith D. E., Gorski J. Extrogen control of uterine glucose metabolism. An analysis based on the transport and phosphorylation of 2-deoxyglucose. J Biol Chem. 1968 Aug 25;243(16):4169–4174. [PubMed] [Google Scholar]


