Fig. 4.
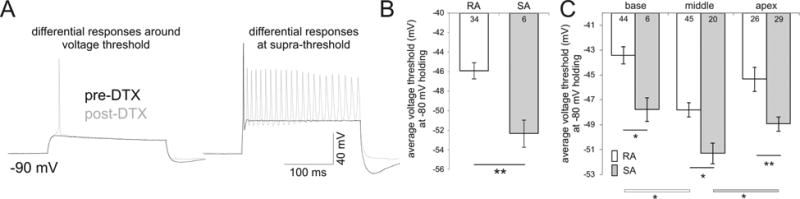
Rapidly accommodating (RA) neurons have significantly higher thresholds than slowly accommodating neurons (SA). (A) Transformation of rapidly accommodating neurons by α-DTX into slowly accommodating neurons occurs in conjunction with significantly altered threshold levels by α-DTX. Left set of traces show that at similar plateau voltages the same neuron that was originally below threshold prior to α-DTX application fired above threshold afterwards. Right set of traces demonstrate the accommodation differences before and after α-DTX application at supra-threshold levels. See text in Results section for RA versus SA distinction. (B) Average threshold comparison between RA and SA neurons demonstrating that RA neurons have higher average thresholds than SA neurons from a subset of recordings shown in Fig 1C. (C) Consistent and significant differences in voltage thresholds from base to apex are preserved in each category when RA and SA neurons are further separated by tonotopic region. Significant differences were observed between RA and SA neurons for each region (p < 0.01), between base and middle for RA neurons (p < 0.05) and between middle and apex for SA neurons (p < 0.05). The differences in the number of recordings between panels B and C reflect the inclusion of previously unpublished analysis (Liu and Davis, 2007) to power these comparisons. Note that the middle RA neurons displayed slightly reduced thresholds from their apical counterparts, yet differed significantly from the basal neurons (white bar with asterisk). When threshold level is evaluated for SA neurons, however, the values for middle neurons are significantly lower than apical (gray bar with asterisk) and slightly lower than basal neurons. The lack of significant difference between middle and base SA neurons is expected as only a small portion of SA neurons (N = 6) can be identified in the base.
