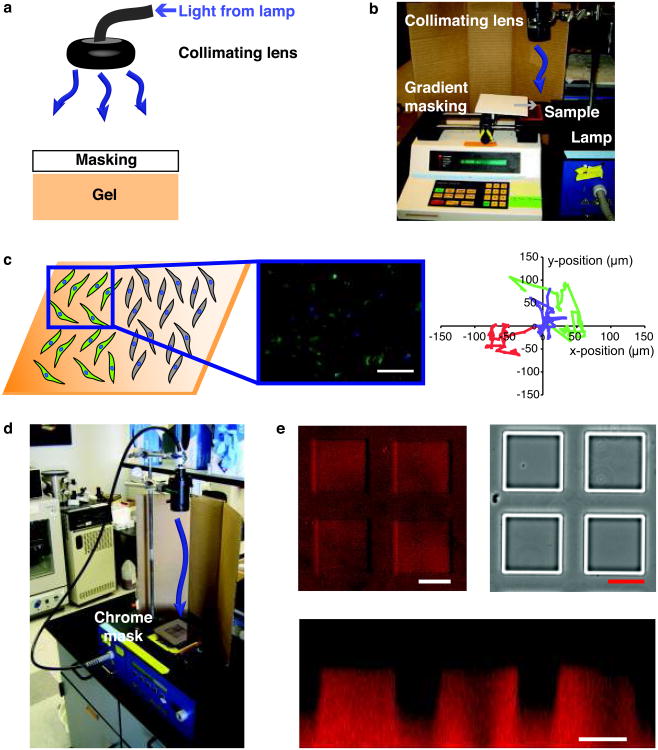
Figure 8. Photopatterning with photolithography.
(a) To pattern photolabile hydrogels with standard photolithography, a mask is placed between a collimated light source and the gel surface. For proper pattern transfer, it is important that the light be well collimated with a collimating lens and that the mask be appropriately placed above the hydrogel surface. (b) Photopatterning can be used to form gradients in elasticity or biochemical signals in photolabile hydrogels via gradient masking. Briefly, the sample is placed in a PBS or medium-filled chamber, and a syringe pump is used to slowly cover the sample so that the sample receives a gradient of light, which induces a gradient in photocleavage. (c) Gradients substrate modulus in 2D can be used to screen its effect on cell functions such as differentiation (left). With modulus gradients created via photodegradation, the minimum modulus for activation of valve fibroblasts into myofibroblasts, a wound healing cell phenotype, was established and assayed by immunostaining for α-smooth muscle actin (αSMA green; nuclei blue) (middle)26. Cell migration in response to modulus can also be assayed on these substrates (right, traces of the x-y position of individual cells taken in 15-min intervals over 3 days)26. While a static gradient is shown here, the steepness and direction of the gradient can be changed temporally in the presence of cells with irradiation. Findings from 2D can subsequently be translated to 3D culture with the same gel formulation for comparison of cell response in 2D and 3D. Scale bar, 100 μm. Copyright Elsevier. Reproduced with permission. (d) Photopatterning can also be employed to generate features at the surface of photolabile hydrogels using a chrome mask. To ensure pattern transfer, use a well-collimated light source and rest the chrome mask just above the gel surface on glass slides or cover glass. (e) Here, we used a mask with square features to pattern positive square pillars on the surface of photodegradable hydrogels. Features are shown in a confocal surface image (upper left), brightfield image (upper right), and confocal cross section image (bottom). Scale bars, 100 μm.