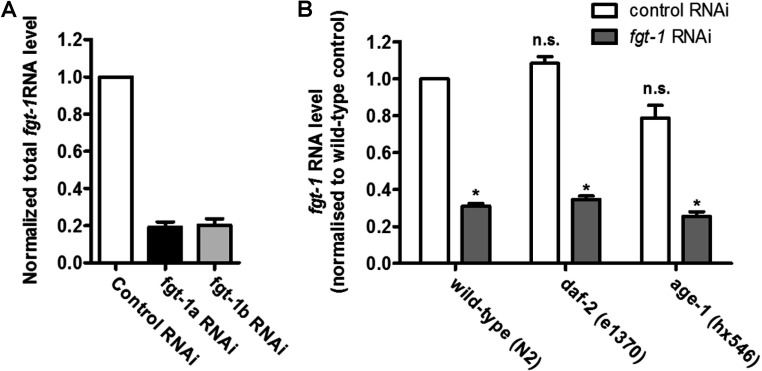
Figure 3. Knockdown of fgt-1a and fgt-1b in wild-type and signalling mutant C. elegans strains.
(A) C. elegans wild-type strain (N2) L1 larvae were seeded on to NGM plates seeded with fgt-1a or fgt-1b RNAi bacteria (with or without 1 mM IPTG to induce knockdown). The young adult worms were transferred on to NGM plates (50 μM FUDR, with or without 1 mM IPTG) seeded with fgt-1a or fgt-1b RNAi bacteria. The worms were maintained on the plates without exhaustion of bacteria food source for 10 days. Total RNAs of each sample were extracted and the extent of knockdown of the total fgt-1 mRNA was determined by qPCR using primers to a region present in both transcripts. Results are means±S.E.M. for three separate experiments. (B) C. elegans L1 larvae of wild-type strain (N2) or strains mutated in the DAF-2 receptor [daf-2 (e1370)], or the PI3K [age-1 (hx546)] were seeded on to NGM plates seeded with fgt-1a and fgt-1b RNAi bacteria mixture (1:1 ratio) (with or without 1 mM IPTG to induce knockdown). The young adult worms were transferred to NGM plates (50 μM FUDR, with or without 1 mM IPTG) seeded with fgt-1a and fgt-1b RNAi bacteria mixture (1:1 ratio). The worms were maintained on the plates without exhaustion of bacteria food source for 10 days. Total RNA of each sample were extracted and the extent of knockdown of the total fgt-1 mRNA was determined by qPCR using primers to a region present in both transcripts. Results are means±S.E.M. for three separate experiments. *P<0.05 compared with the uninduced control. mRNA levels in mutant strains daf-2 and age-1 were not significantly different (n.s.) compared with the wild-type strain (P=0.072 and 0.075 respectively).