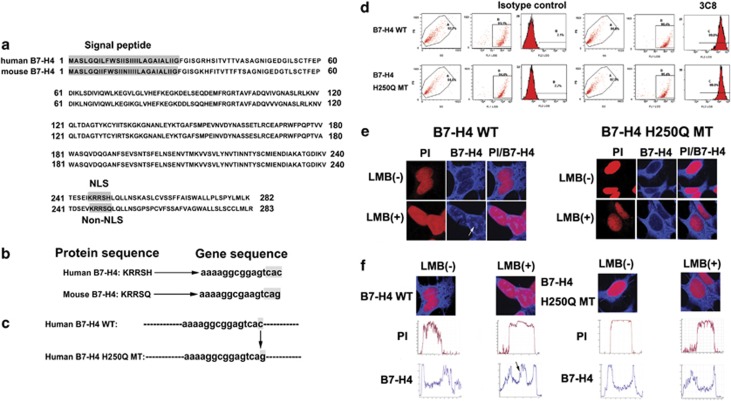
Figure 2.
The NLS motif in B7-H4 protein. (a) Comparison of human and mouse B7-H4 sequence. Signal peptide and NLS motif were shaded in gray. (b) Contrast to human B7-H4, mouse homolog lacks a consensus NLS motif. The crucial nucleotides for NLS were shaded in gray. (c) A point mutation of human B7-H4 NLS motif. At nucleotide position 750, C was changed to G, resulting in a change from His to Gln at amino acid position 250. (d) Flow cytometric analysis of either B7-H4 WT/293 or B7-H4 H250Q MT/293 transfectants showed that the stable transfected cell lines were successfully constructed. (e) The B7-H4 transfectants and B7-H4 H250Q transfectants were examined by confocal immunofluorescent microscopy in the absence or presence of LMB. The anti-B7-H4 mAb 3C8 was used. White arrows indicated the nuclear localization of B7-H4 (PI (red, DNA) and cy5 (blue, B7-H4)). (f) The merged images were subjected to line intensity scan using Leica LAS AF software to assess the localization of B7-H4. Intensity profiles corresponding to the lines were determined using Leica LAS AF software. Y- and X-axes represent the level of fluorescence and scanning position, respectively. The black arrows indicated the presence of blue fluorescence in red fluorescence, which suggest the existence of B7-H4 in nucleus.