Fig. 7.
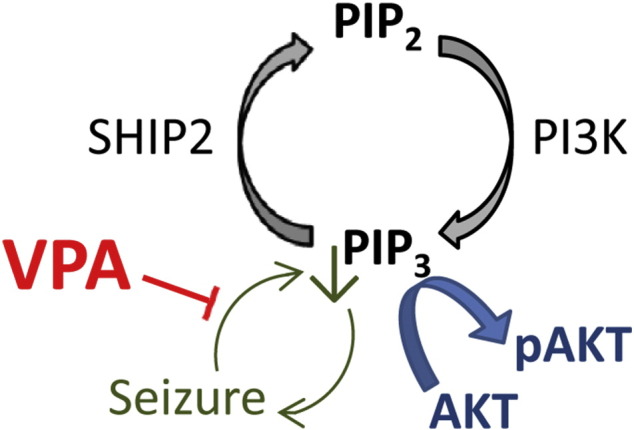
Action of valproic acid (VPA) in regulating PIP3 during seizure activity. Phosphoinositide signalling (black) involves the phosphorylation of PIP2 to produce PIP3 by PI3K activity, and where the reverse reaction is catalysed by SHIP2 activity. PIP3 functions to regulate a range of cellular effects including the activation of downstream AKT activity (blue) by phosphorylation. Seizure activity (green) triggers a decrease in PIP3 giving rise to a feed-back amplification effect. VPA functions to attenuate the seizure-dependent decrease in PIP3 causing a resultant reduction in seizure activity.
