Figure 1.
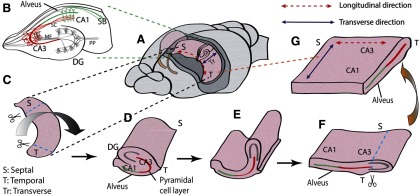
Unfolded hippocampal preparation. A, The two hippocampi were dissected from septal to temporal lobe. B, Typical hippocampal transverse slice with a well-known trisynaptic pathway in the transverse direction. Neural signals coming from the entorhinal cortex propagate through the perforant path (PP) to the granule cells in the DG, to the CA3 through the mossy fibers (MF), to the CA1 neurons, and to subiculum (SB). C, A single whole hippocampus removed using custom-made glass pipette tools. Septal and temporal ends were cut off before unfolding. D, Flipped hippocampus with a clear transverse side. A sharp glass needle was used to cut off the perforant path along hippocampal fissure, and a thin wire loop was inserted into hippocampal fissure to pull over the DG. E, DG was pulled to further flatten the unfolded curved structure. F, After unfolding, the alveus is positioned at the bottom, and the cell layer is nearly flat. The DG was cut off, leaving both CA3 and CA1. G, The final unfolded preparation contains both longitudinal and transverse paths of the pyramidal cells.
