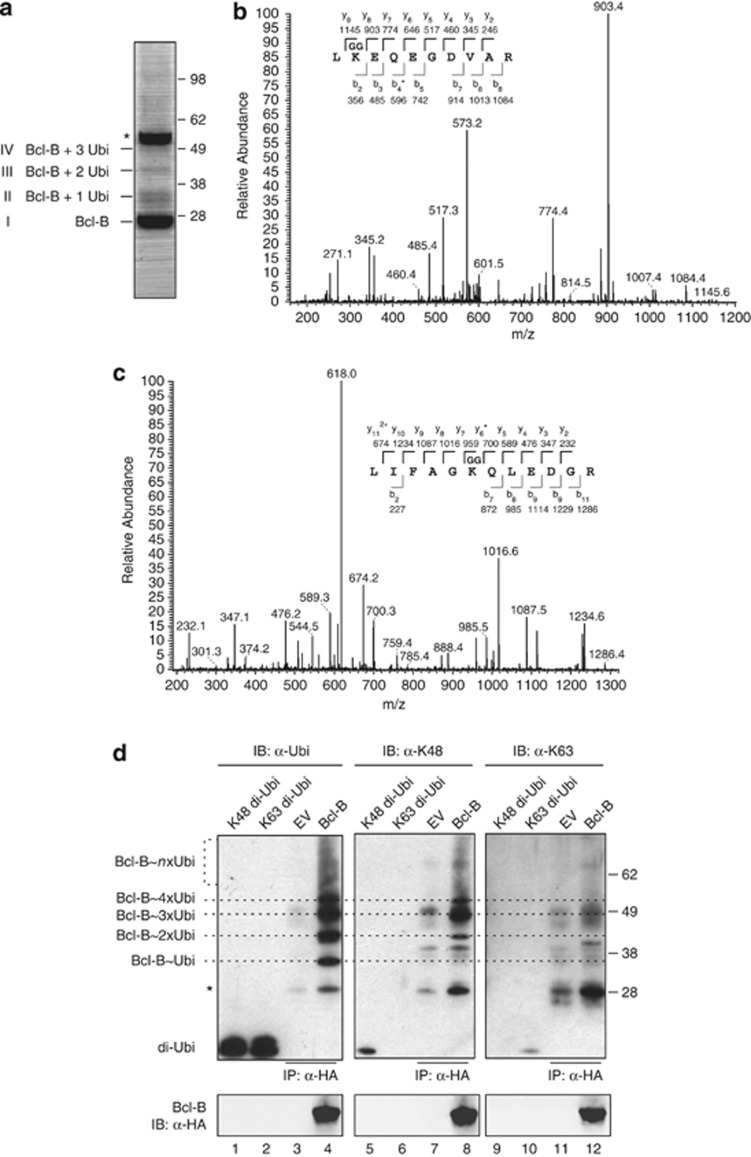
Figure 2.
Bcl-B is ubiquitinated on K128 by K48-linked chains. (a) HEK 293 T cells were transfected to express N-terminally HA-tagged Bcl-B and subsequently lysed under denaturing conditions. HA-Bcl-B was purified by sequential anti-HA IP using two anti-HA mAb clones, as described in the Materials and methods section. The isolate was analyzed by SDS–polyacrylamide gel electrophoresis (SDS–PAGE) followed by Coomassie SimplyBlue staining. The asterisk indicates the heavy chain band of the antibody used for IP. (b) Purified protein in the respective bands identified in a was digested in gel with trypsin, and liberated peptides were analyzed by nanoLC-MS/MS. Depicted is the tandem mass spectrum of fragmented Bcl-B peptide, containing GG-modified K128. The amino acid sequence of the tryptic peptide with identified y and b ions and their masses is shown. The asterisk indicates the identified b4 ion minus NH3. (c) Same as b, but showing the tandem mass spectrum of fragmented ubiquitin peptide, containing GG-modified K48. The asterisk indicates the identified y6 ion minus NH3. (d) Anti-HA IP samples, isolated as in a from HEK 293 T cells expressing HA-Bcl-B or empty vector (EV), were separated by SDS–PAGE. On the same gel, 100 ng of synthetic K48- or K63-linked di-ubiquitin were loaded (di-Ubi). After blotting, the samples were probed with anti-HA to detect Bcl-B, with anti-ubiquitin P4D1 to detect all ubiquitin species (α-Ubi,) and with the K48- or K63-linkage-specific ubiquitin antibodies (α-K48, α-K63). Dotted lines indicate ubiquitinated species of Bcl-B as detected in α-Ubi blot, specifying the presence of one (Ubi), two, three, four or more ubiquitins, based on the molecular mass. Asterisk indicates some cross-reactivity with the light chain of the antibody used for IP and comigrating nonubiquitinated Bcl-B that were visible by Ponceau S staining. Data shown are representative of multiple independent experiments.