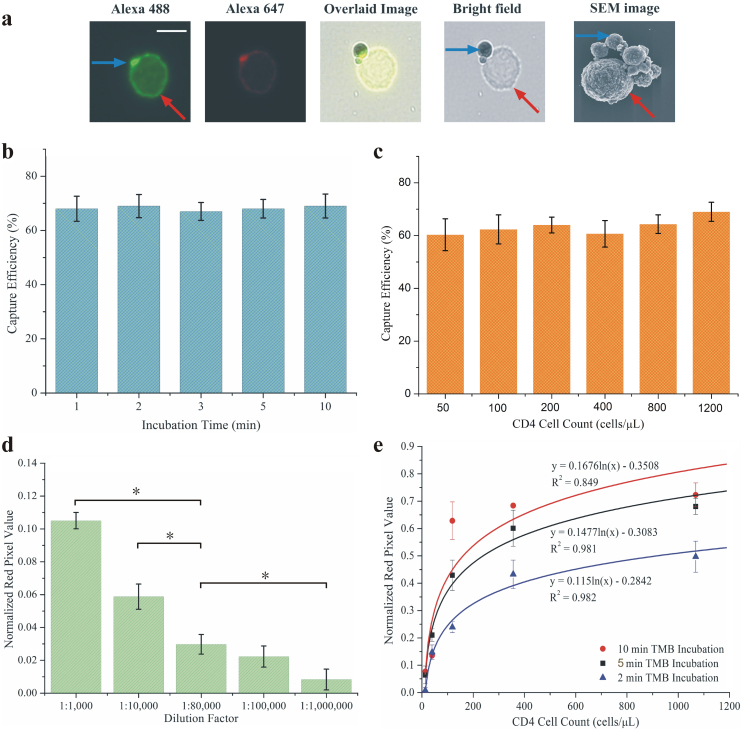
Figure 2. Characterization of m-ELISA for CD4 cell count.
(a) Capture of CD4+ T lymphocytes (red arrow) on magnetic beads (blue arrow). Magnetic beads were incubated with whole blood and the captured T lymphocyte was stained with anti-CD4 Alexa Fluor 488 and anti-CD3 Alexa Fluor 647. The fluorescent images of Fluor 488, Alexa Fluor 647, bright-field, as well as the overlaid image (by ImageJ software) demonstrate capture of CD4+ T lymphocytes by magnetic beads. The scanning electron microscope (SEM) image validates the capture of CD4+ T lymphocyte on magnetic beads. The scale bar is 10 μm. (b) Efficiency of magnetic beads for capturing CD4+ T lymphocytes at varying incubation times. 25 μL of functionalized magnetic beads (10 mg/mL) were incubated with whole blood containing 1,000 cells/μL CD4+ T lymphocyte. The unbound T lymphocytes in the supernatant were quantified by flow cytometry, which was used to calculate the capture efficiency. One-way ANOVA was performed to analyze and no statistical significance (p > 0.05) was found. (c) Efficiency of magnetic beads for capturing CD4+ T lymphocytes at varying concentrations of CD4+ T lymphocytes. The same procedure as mentioned in (b) was used to calculate the capture efficiency. One-way ANOVA analysis indicated that there was no significant difference in capture efficiency (p > 0.05). (d) Optimization of HRP-antibody in m-ELISA. The variable, HRP-conjugated antibody was diluted at different concentrations and tested with plasma samples, which served as negative control. 1:80,000 was chosen for the following experiments since this concentration was the highest concentration of HRP-antibody that avoided false positive results. A mobile application was used to extract red (R) pixel values from the color development region on-chip and normalized them according to the background as shown in the Y-axis. One-way ANOVA was performed to analyze the color intensity caused by excessive HRP (n = 3, * indicates the statistical significance, p < 0.05). (e) Whole blood from a healthy blood sample was serially diluted (undiluted, 1:3, 1:9, 1:27 and 1:81) used to construct the standard curve with different 3, 3′, 5, 5′ Tetramethylbenzidine (TMB) incubation periods. Each data point was performed in triplicates and the standard deviation was shown.