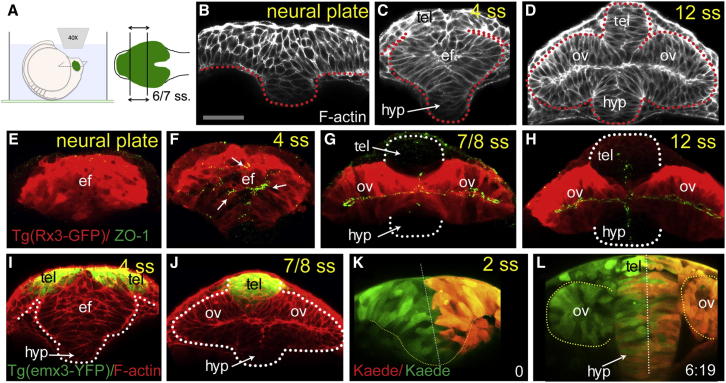
Figure 1.
Reduced Convergence and Precocious AB Polarization of Eye Field Cells
(A) These panels and those in other figures show transverse (frontal) confocal sections through the developing ANP at the level of the eye field/optic vesicles, imaged as schematized in (A).
(B–D) Wild-type embryos stained with F-actin to reveal cellular organization. tel, telencephalon; ef, eye field; hyp, hypothalamus; ov, optic vesicle. Scale bar, 64 μm (B).
(E–H) Tg(rx3:gfp) embryos immunostained against GFP (red) and ZO-1 (green/yellow, arrows in F) to reveal cell polarity.
(I and J) Tg(emx3:yfp) embryos immunostained against GFP (green) and stained for F-actin (red), showing the reorganization of the telencephalon that accompanies optic vesicle evagination.
(K and L) Initial (K) and final (L) time points of a time-lapse movie sequence of an embryo expressing Kaede. One-half of the neural plate was photoconverted from green to red by UV illumination (t = 0).
White dotted lines in (G) and (H) outline the telencephalon and hypothalamus; red/white lines in (B)–(D) and (K) and (L) outline the neural anlage. See also Figure S1 and Movie S1.