Figure 4.
Metformin Inhibits Bacterial Folate Metabolism
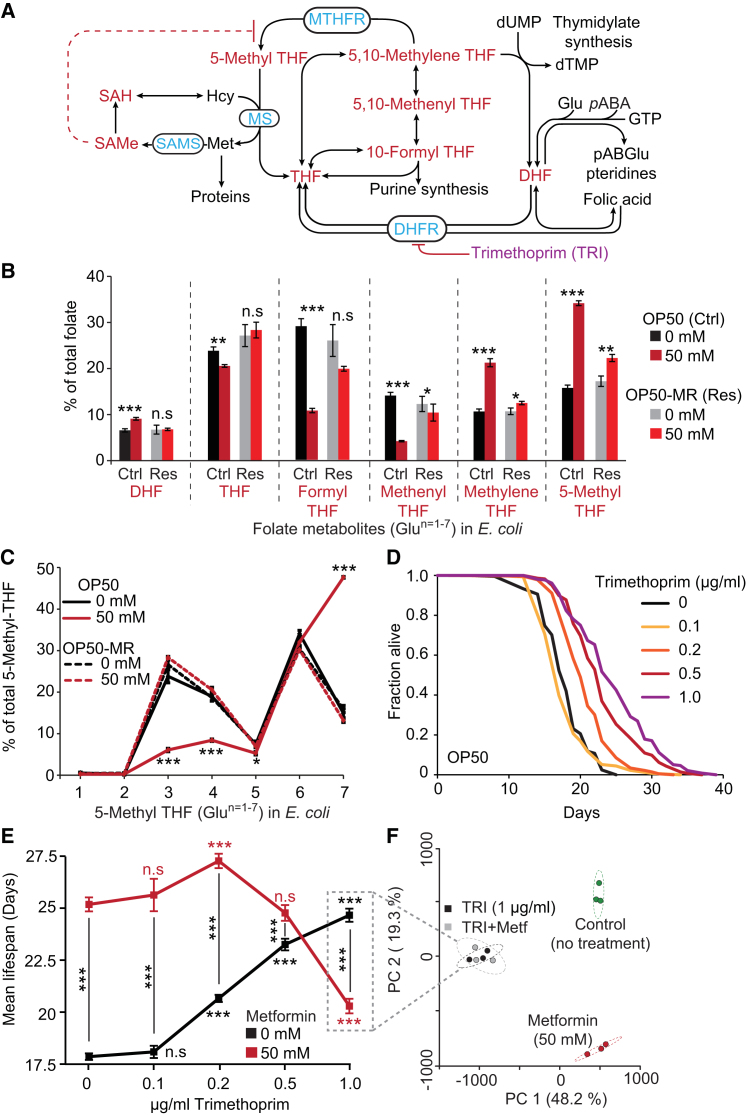
(A) The folate and methionine cycles. Metabolites analyzed, red; enzymes, blue; supplements, purple. DHF, dihydrofolate; DHFR, dihydrofolate reductase; Glu, glutamate; Hcy, homocysteine; Met, methionine; MS, methionine synthetase; MTHFR, methylenetetrahydrofolate reductase; pABA, p-aminobenzoic acid; SAH, S-adenosylhomocysteine; SAMe, S-adenosylmethionine; SAMS, S-adenosylmethionine synthase; THF, tetrahydrofolate; TRI, trimethoprim. Dotted lines represent feedback loops.
(B) Metformin alters folate homeostasis in E. coli OP50 but not OP50-MR. The values for each metabolite are the sum of the values for the different glutamate side chains (1–7) divided by sum of all folate metabolites measured.
(C) Metformin alters 5-methyl-THF polyglutamylation in OP50 but not OP50-MR.
(D) The DHFR inhibitor TRI increases C. elegans lifespan in a dose-dependent manner. See Figure S4D for E. coli growth retardation by TRI.
(E) Effects of metformin and TRI on lifespan are nonadditive, consistent with similar modes of action.
(F) Principal component analysis (Metaboanalyst) of OP50 metabolites with TRI and metformin. Note that TRI abolishes effects of metformin.
Error bars represent SEM. ∗p < 0.05; ∗∗p < 0.01; ∗∗∗p < 0.001. See also Figure S4. For statistics, see Table S4.