Figure 7.
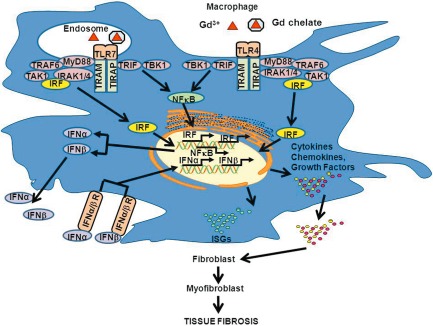
Pathways mediating gadolinium-based contrast agent (GdBCA) induction of a proinflammatory/profibrotic phenotype in normal human macrophages. Cellular recognition of either free Gd3+ (transmetallation model) or of the intact gadolinium chelate (chelate model) is mediated through Toll-like receptor (TLR)-4 and TLR-7 signalling. The signalling events result in up-regulation of X-linked inhibitor of apoptosis (XIAP) and interferon regulatory factor (IRF) genes and activation of nuclear factor kappa B (NFκB), which co-operate to up-regulate type I interferons, that in turn activate type I interferon signature genes (ISGs) resulting in production of proinflammatory and profibrotic chemokines, cytokines and growth factors. These factors are secreted by activated macrophages and can then act to promote the transdifferentiation of quiescent fibroblasts to activated myofibroblasts, characterized by initiation of α-smooth muscle actin (α-SMA) expression and in dysregulated and sustained extracellular matrix production leading to tissue fibrosis. Figure modified from 19.
