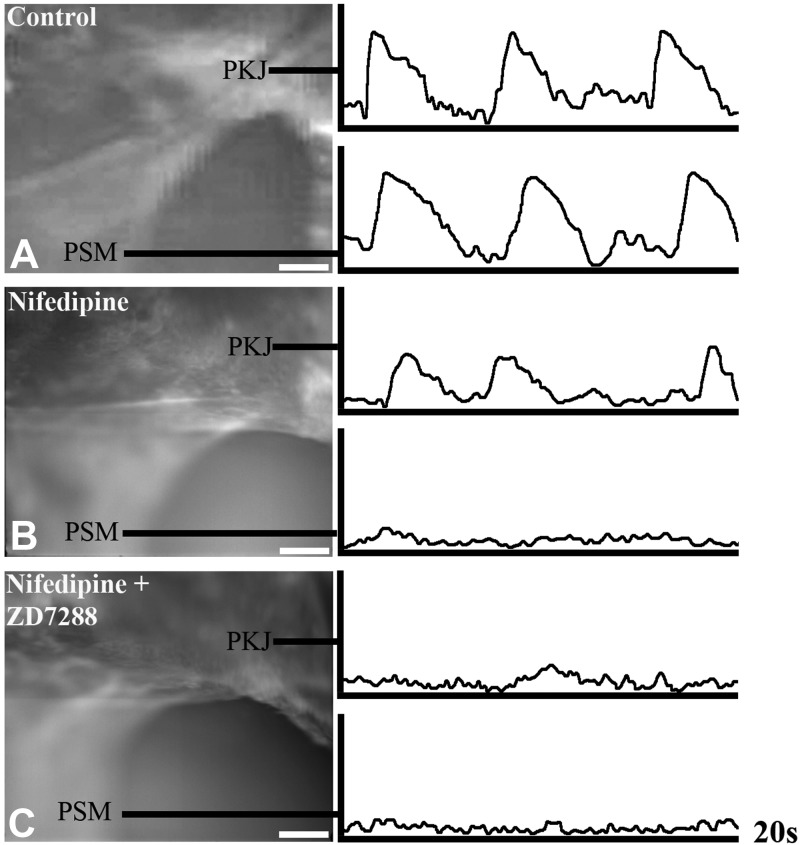
Figure 3.
HCN channel conductance is required for UUT pacemaker activity. To determine whether HCN channel conductance is required for UUT pacemaker activity, we used ratiometeric optical mapping to analyze pacemaker depolarizations with and without HCN channel inhibition. A) UUT explants were loaded with di-4-ANEPPS dye, which undergoes voltage-dependent shifts of dual emission wavelengths. Rhythmic depolarizations detected at the PKJ preceded depolarizations in the more distal pelvic smooth muscle (PSM) in urinary tract explants treated with Tyrode's saline alone (n=6). B) To isolate pacemaker depolarizations from the composite electrical activity at the PKJ, we inhibited smooth muscle excitation via nifedipine (10 μM) block of L-type Ca channels. Nifedipine inhibited the generation and propagation of PSM action potentials, and enabled the detection of spontaneous rhythmic pacemaker depolarizations at the PKJ (n=6). C) To determine whether pacemaker depolarizations elicited at the PKJ are dependent on HCN channel conductance, explants incubated with nifedipine were simultaneously incubated with ZD7288 (30 μM). Pacemaker potentials at the PKJ were abolished by HCN channel block (n=4). Scale bars = 100 μm.