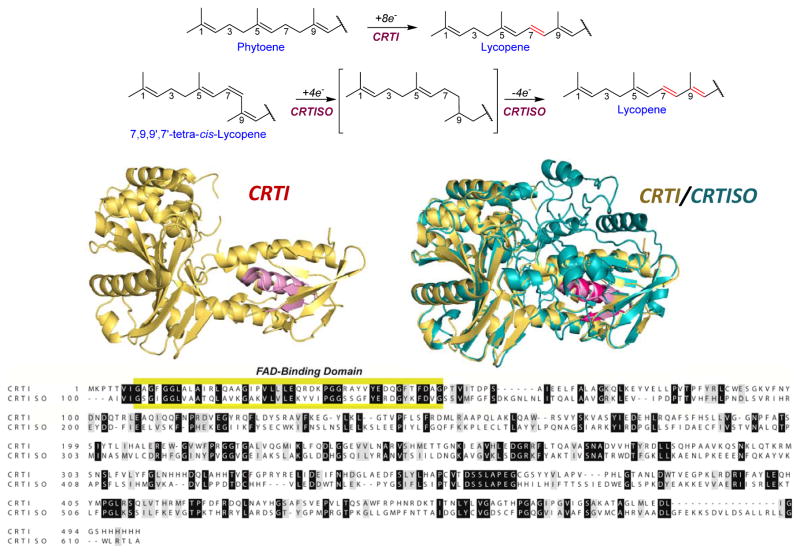
Figure 10.
The enzymatic reaction, structure and key features of CRTI and CRTISO. The desaturation reaction catalyzed by CRTI is shown in comparison with the saturation-isomerization-desaturation reaction catalyzed by CRTISO. Bottom left, the structure of CRTI is based on its reported structure (PDB 4DGK) indicating the FAD binding β-α-β fold (pink). 152c Bottom right, a prediction of the structure of tomato CRTISO using I-TASSER 144 is colored in teal and is superimposed on the CRTI structure colored in gold. The FAD binding domain of CRTISO (purple) and that of CRTI (pink) are indicated. Below, the alignment of the sequence of hexahistidine tagged-CRTI (as used to generate the PDB 4DGK structure) and tomato CRTISO with identical residues in white letters on black background and conserved substitutions in black on grey background. The extended FAD binding domain shared by CRTI, CRTISO and protoporphyrinogen oxidoreductases and monoamine oxidase is highlighted in yellow. The diagrams depicting reactions of CRTI and CRTISO is adapted and reprinted with permission from reference from reference 197b. Copyright 2005 Elsevier.