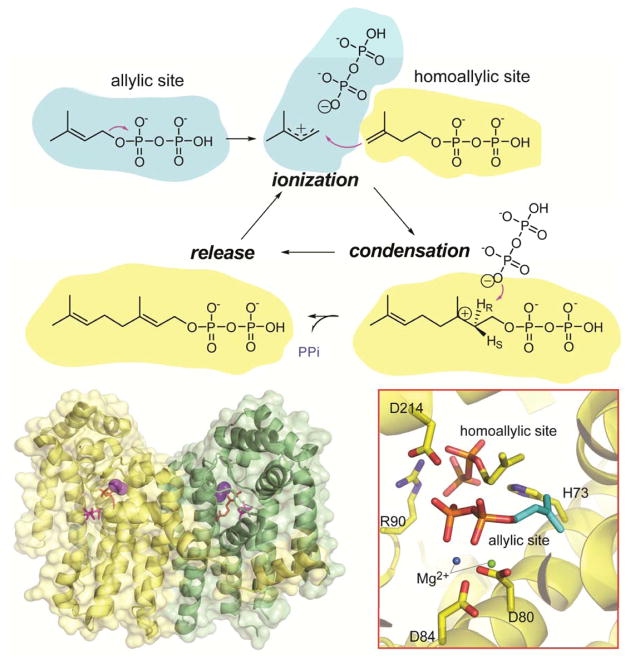
Figure 8.
The mechanism of cyclic condensations, structure and key features of GGPPS. Top, mechanism of the 1′-4 head-to-tail condensation condensation reaction catalyzed by GGPPS. The allylic substrate (DMAPP shown) binds the allylic binding site in blue while IPP binds to the homoallylic binding site indicated in yellow. The condensation cycle proceeds through ionization, condensation and release steps. Bottom, the structure of GGPPS dimer (green and yellow subunits) in association with isoprenoid substrates (red) based on its published structure (PDB 2E8U). 130b Inset shows the orientation of IPP bound to either the natural, homoallylic binding site or the non natural allylic binding site of GGPPS. Binding to the allylic site is mediated by the Mg2+ cluster which is coordinated by the residues D80, D84 of the DDxxD motif. Active site residues R90, D214 and H73 that are proposed to participate in substrate binding are also shown (residues and substrate IPP are colored by heteroatoms). The mechanism of reaction of GGPPS is adapted and reprinted with permission from Reference 284. Copyright 2008 American Chemical Society.