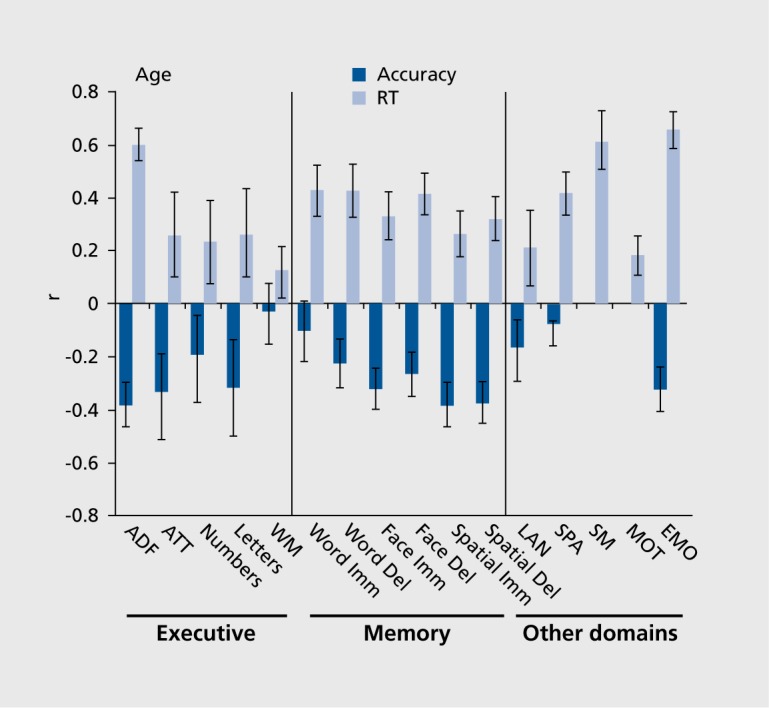
Figure 3. Correlations of age with accuracy (black bars) and response time (RT; gray bars) indices of performance on the tests. Error bars indicate 95% confidence intervals based on 1 000 bootstraps. As seen, the effects of age are stronger for speed than for accuracy, and more pronounced for abstraction/flexibility and episodic memory than for attention and working memory. ABF, abstraction and mental flexibility; ATT, attention; WM, working memory; Imm, immediate; Del, delayed; LAN, language reasoning; SPA, spatial processing; SM, sensorimotor speed; MOT, motor speed; EMO, emotion processing Reproduced from ref 19: Gur RC, Richard J, Hughett P, et al. A cognitive neuroscience-based computerized battery for efficient measurement of individual differences: standardization and initial construct validation. J Neurosci Methods. 2010;187:254-462. Copyright © Elsevier 2010.