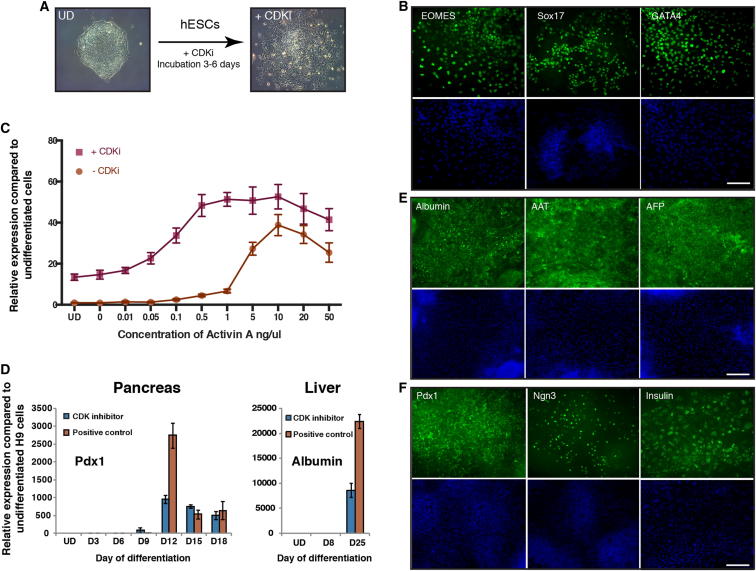
Figure 7.
CDKi Treatment Induces Differentiation of hPSCs
(A) Representative colonies of untreated hESCs and CDKi (0.75 μM PD0332991)-treated cells.
(B) CDK4/6 inhibition results in endoderm differentiation. hESCs grown for 6 days in the presence of CDKi (0.75 μM PD0332991) were analyzed for the expression of germ layer markers using immunofluorescence microscopy.
(C) CDK4/6 can replace Activin A during endoderm differentiation. H9 cells were incubated in the presence or absence of 0.75 μM CDKi in standard endoderm differentiation conditions and analyzed for Sox17 expression by qPCR.
(D and E) Endoderm cells generated by CDKi can give rise to cells expressing hepatic markers. CDKi-produced endoderm was grown for 25 days in culture conditions for hepatic differentiation and then the expression of hepatocyte markers was analyzed using qPCR (D) or immunostaining (E).
(F) Endoderm generated by CDKi can give rise to pancreatic cells. CDKi produced endoderm was grown for 18 days in culture conditions for pancreatic differentiation and then the expression of pancreatic markers was analyzed using qPCR (D) or immunostaining (F). Scale bar represents 100 μm. All data are shown as mean ± SD (n = 3). UD, undifferentiated cells.
See also Figures S5, S6, S7, and Table S5.