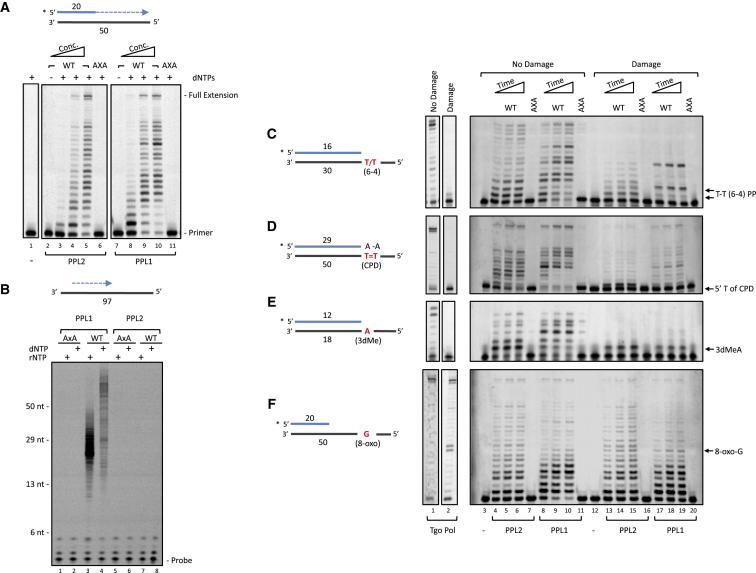
Figure 5.
TbPPL1 and TbPPL2 Are DNA-Dependent Translesion DNA Polymerases
(A) DNA synthesis by His-tagged TbPPL1 and TbPPL2. Primer template substrate (20 nM) containing a 5′ fluorescent label on the primer strand and dNTPs (200 μM) were incubated without (−) or with wild-type (WT) TbPPL1 or TbPPL2 (50, 125, 250 nM) or catalytic (AxA) mutants (250 nM) for 30 min at 37°C.
(B) Primer synthesis by TbPPL1 and TbPPL2. A single-stranded DNA template (500 nM) of variable sequence was incubated with either dNTPs or rNTPs (500 μM) and TbPPL1 or TbPPL2 (1 μM) for 2 hr at 37°C, and products were detected as described in Experimental Procedures.
(C–F) DNA synthesis by TbPPL1 and TbPPL2 on templates containing a T-T pyrimidine (6-4) pyrimidone photoproduct (6-4 PP) (C), a T-T cis-syn cyclobutane pyrimidine dimer (CPD) (D), a 3-deaza 3-methyladenine (3dMeA) (E), and an 8-oxo-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-oxo-G) (F). (C), (E), and (F) contain substrates with primer termini 3′ of the templated lesion, thereby testing read-through of the lesion, while the primer in (D) contains two 3′ terminal dA residues annealed opposite the CPD, thereby testing extension from the lesion. Primer extensions performed as in (A) except with 125 nM TbPPL1 or TbPPL2 for 10, 20, and 30 min or just a single 30 min time point. As a control the archaeal family-B replicase Tgo-Pol exo− (100 nM) was used.