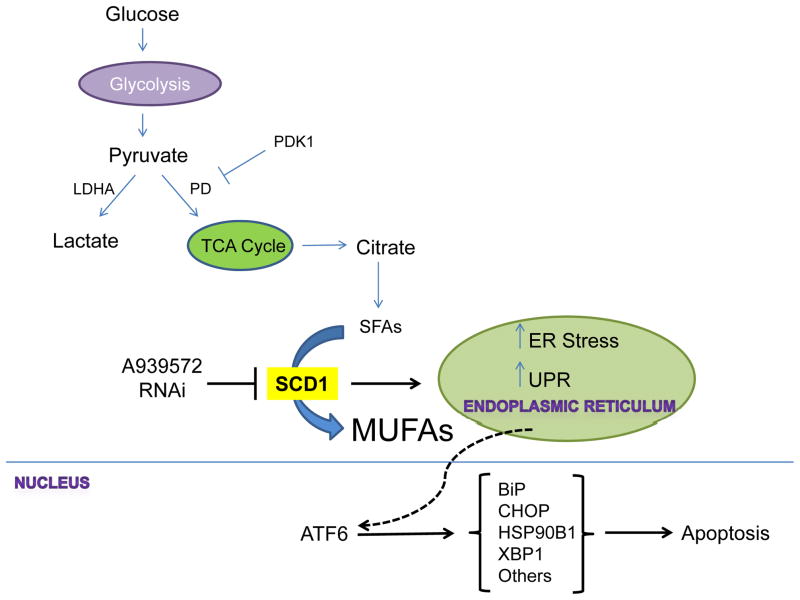
Figure 1.
Glycolysis results in the production of pyruvate, which can be converted to acetyl-CoA (not shown) by pyruvate dehydrogenase (PD). PD activity can be suppressed by pyruvate dehydrogenase kinase (PDK1) whereby pyruvate is then directed towards lactate production by lactate dehydrogenase A (LDHA). Acetyl-CoA enters the TCA cycle and is converted to citrate, a portion of which is diverted towards fatty acid synthesis. Saturated fatty acids (SFAs) are converted to monounsaturated fatty acids (MUFAS) by stearoyl Co-A desaturase (SCD1). SCD1 inhibition by RNAi or A939572 results in the unfolded protein response (UPR) and increased ER stress resulting in the increased production of ATF6, which activates expression of genes mediating stress response pathways (BiP, CHOP, HSP90B1 and XBP1). Under prolonged ER stress the cell responds by initiating apoptosis.