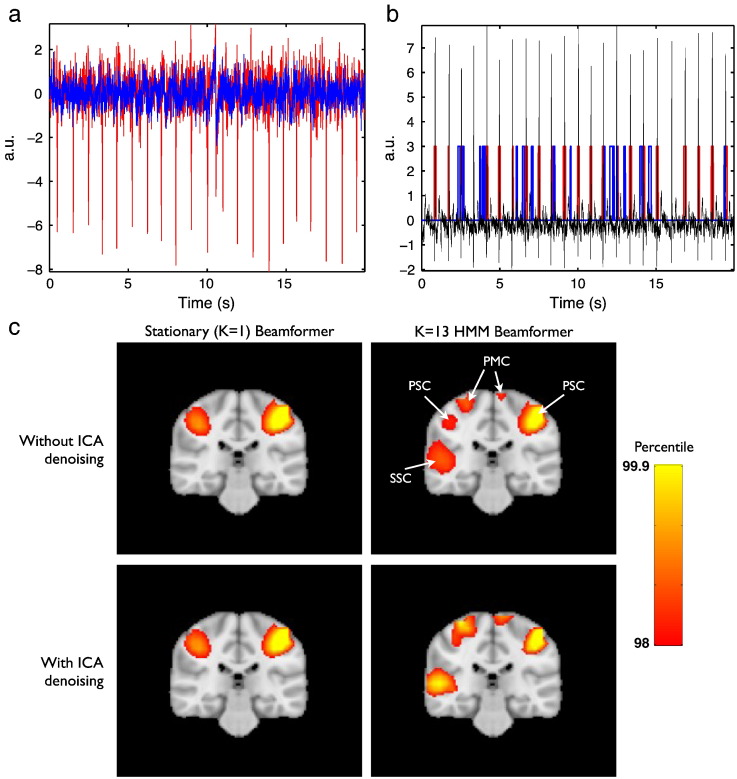
Fig. 11.
Effects of ICA denoising. (a) First 20 s of sensor time course for the sensor showing the highest correlation with the main ECG IC time course, before (red) [correlation = − 0.82] and after (blue) [correlation = − 0.03] removal of the IC component corresponding to the ECG artefact. (b) First 20 s of HMM state time courses for the HMM state with the highest correlation with the main ECG IC time course when running the HMM inference on data, before (red) [correlation = 0.23] and after (blue) [correlation = 0.02] removal of the IC component corresponding to the ECG artefact. The IC time course identified as the ECG artefact is shown for comparison (black). (c) Comparison of standard stationary beamformer [left] and a 13 state HMM beamformer [right], for the finger-tapping MEG dataset, shown with [bottom] and without [top] ICA denoising having been applied in sensor space. Images show the z = − 28 mm slice of the uncorrected t-statistic spatial maps.