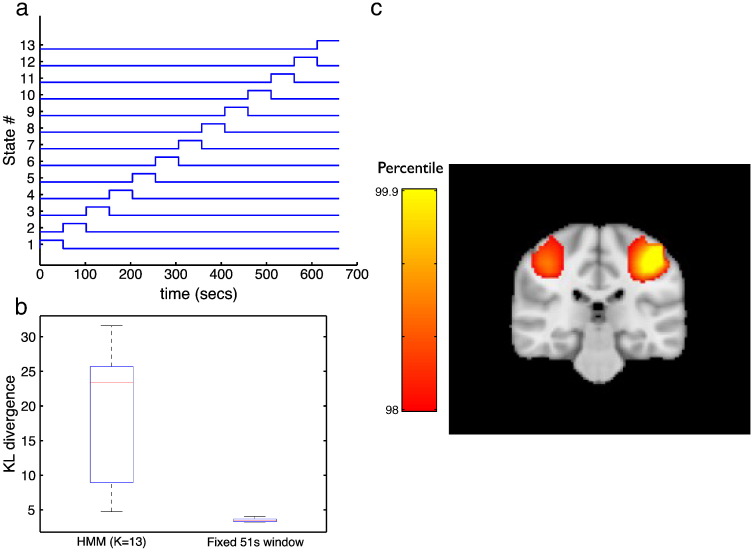
Fig. 12.
Fixed sliding time window approach (with window width 51 s). This is equivalent to the HMM approach but where the HMM state time courses are fixed as shown in (a) (rather than inferred from the data). (b) Shown is the distribution of the KL divergences between the full stationary data covariance matrix and the data covariance matrices estimated using (left) the HMM state time courses for the K = 13 HMM approach, and (right) the fixed sliding time courses shown in (a). (c) Shown is the result of using the fixed sliding time window beamformer approach for comparison with the maps in Fig. 10.