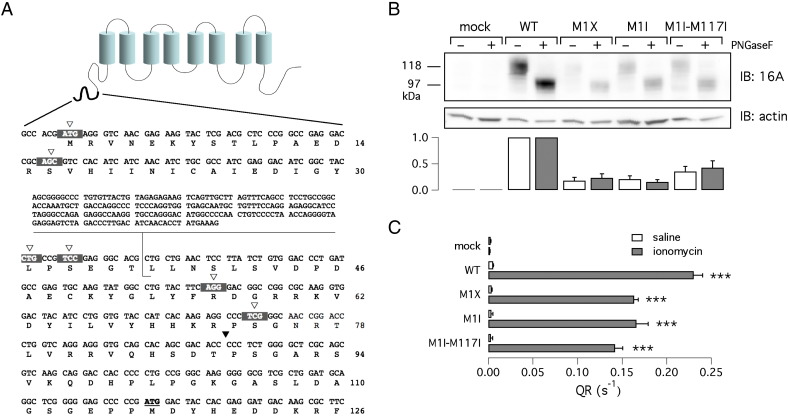
Fig. 1.
Analysis of TMEM16A translation start site. A) TMEM16A topology and amino acid sequence of the TMEM16A amino-terminus. The alternative 5′-untranslated region of the cDNA clone BC033036 is shown as an inset. White triangles and the black triangle show sites where the stop codon mutations and the HA epitope were introduced, respectively (for the experiments reported in Fig. 3). B) Electrophoretic mobility of wild type and mutant TMEM16A proteins as detected in western blot experiments (with anti-TMEM16A SP31 antibody). The first ATG was replaced with a nonsense (M1X) or an isoleucine (M1I) codon. A double mutant with methionines 1 and 117 replaced by isoleucine was also studied (M1I-M117I). Where indicated, cell lysates were treated with PNGaseF to remove sugars. Densitometric analysis of TMEM16A expression from four experiments is shown in the bar graph. The intensity of the band in each sample was normalized to the expression of actin and then to the expression of wild type TMEM16A (white bar for glycosylated samples, gray bar for deglycosylated samples). C) Activity of wild type and mutant TMEM16A determined with the HS-YFP assay. Activity, reported as quenching rate (QR), was determined with and without 1 μM ionomycin (***, p < 0.001 vs. mock-transfected cells; n = 5–6).