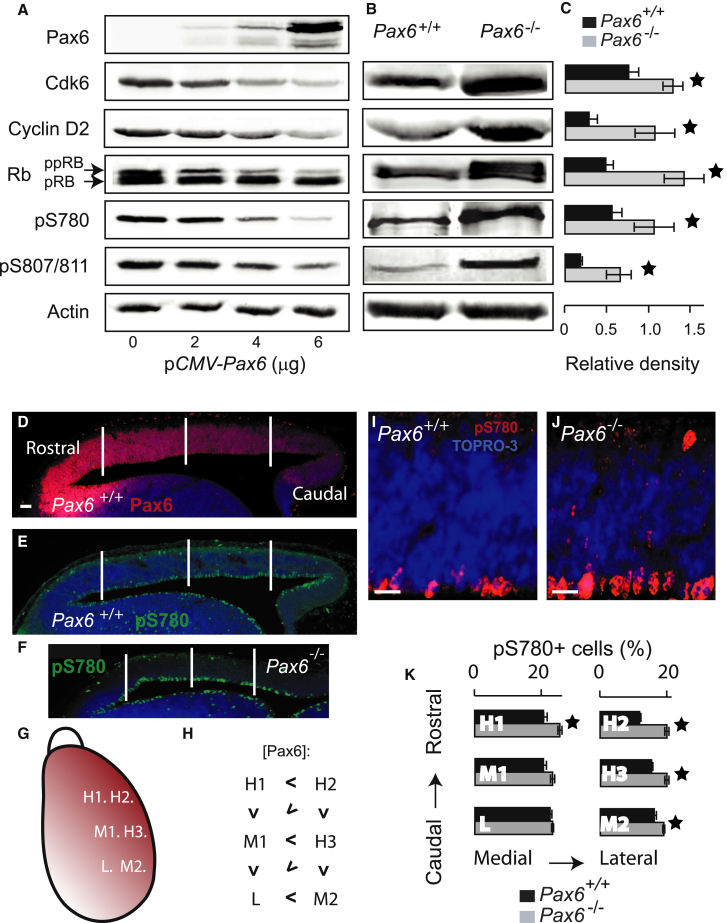
Figure 6.
Pax6 Suppresses Hyperphosphorylation of pRb
(A) Western blots showing that transient transfection of HEK293 cells with increasing amounts of Pax6 expression plasmid pCMV-Pax6 resulted in increasing levels of Pax6 and decreasing levels of Cdk6, cyclin D2, the hyperphosphorylated form of pRb (ppRB), pRb phosphorylated at serine 780 (pS780), and pRb phosphorylated at serine 807/811 (pS807/811). Similar results were obtained in three independent experiments.
(B) Western blots on protein extracted from E12.5 cortices showing increased levels of Cdk6, cyclin D2, ppRb, pS780, and pS807/811 in the absence of Pax6.
(C) Densitometry on bands representing Cdk6, cyclin D2, pRb, pS780, and pS807/811 from western blots such as those in (B). For each protein extract, values were normalized to the β-actin level in that sample. Means ± SEM; ∗p < 0.05, Student’s t test; n = 3 independent experiments in each case.
(D–F) Immunohistochemistry showing expression of pS780 and Pax6 in parasagittal sections of E12.5 Pax6+/+ and Pax6−/− cortex. Vertical lines mark the rostrocaudal levels of the quantifications in (G), (H), and (K); counts were in 150 μm × 30 μm areas oriented along the ventricular surface. Scale bar, 100 μm.
(G–K) Quantification of the percentages of pS780+ cells in three cortical areas expressing relatively high (H1–H3), medium (M1 and M2), and low (L) levels of Pax6 in two rostral-to-caudal rows of sampling areas (one row medial to the other, laid out as illustrated on a dorsal view of the right hemisphere in (G). The relationships between the relative levels of Pax6 in each position [<] are summarized in (H).
(I and J) Rostrolateral sections of cortex from E12.5 Pax6+/+ and Pax6−/− embryos immunoreacted for pS780. Scale bars, 25 μm.
(K) Means ± SEM; ∗p < 0.05, Student’s t test; n = 9 embryos of each genotype.
See also Figure S7.