Fig. 2.
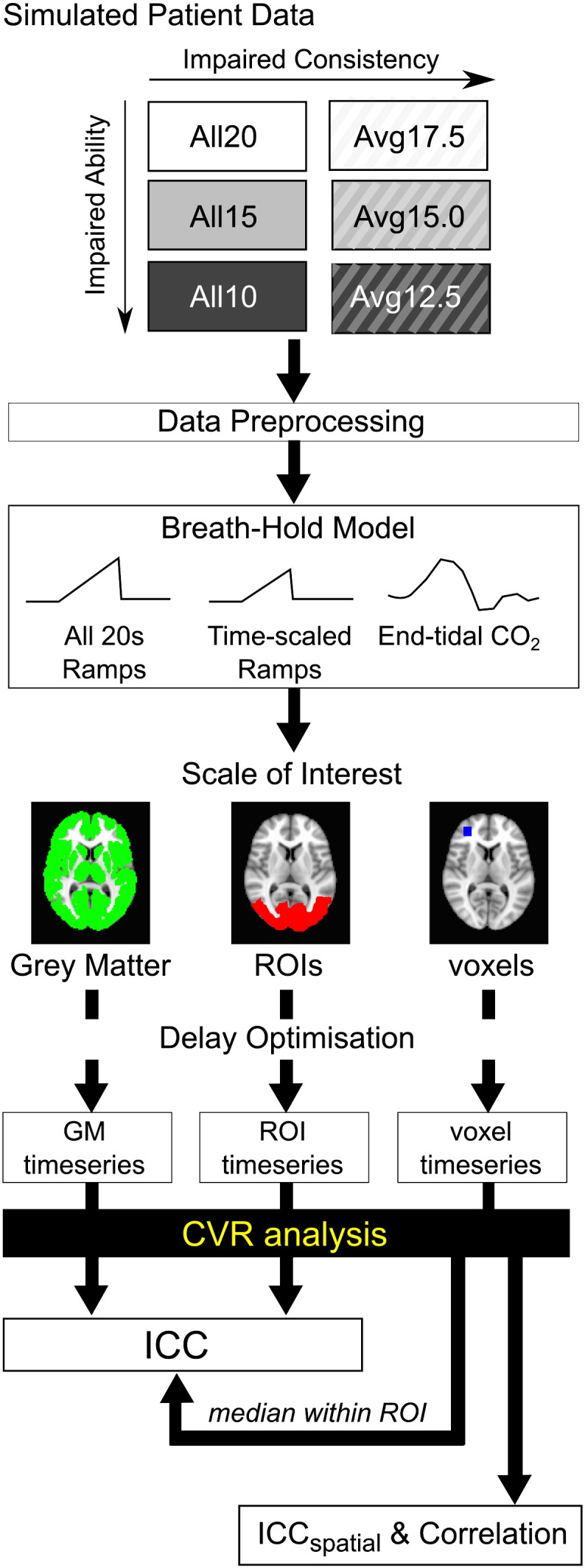
Schematic of analysis pipelines used in this study. Six breath-hold scans were acquired to simulate varying levels of ability and consistency. Following standard data preprocessing, CVR was calculated as follows: a breath-hold model was selected, a scale of interest defined, and an optimal delay time between breath-hold regressor and data determined prior to including the regressor in a general linear model. CVR results obtained using grey matter or ROI mean timeseries, as well as the median CVR value obtained from voxelwise values, were used to calculate the intraclass correlation coefficient (ICC) across the 12 subjects and 6 scans. The ICC quantifies the repeatability of a subject's CVR measure despite poor breath-hold performance. The voxelwise CVR values were also compared within an individual subject dataset using correlation analysis and ICCspatial; both of these parameters assess the consistency of spatial patterns of voxelwise CVR values within the grey matter of one subject.
