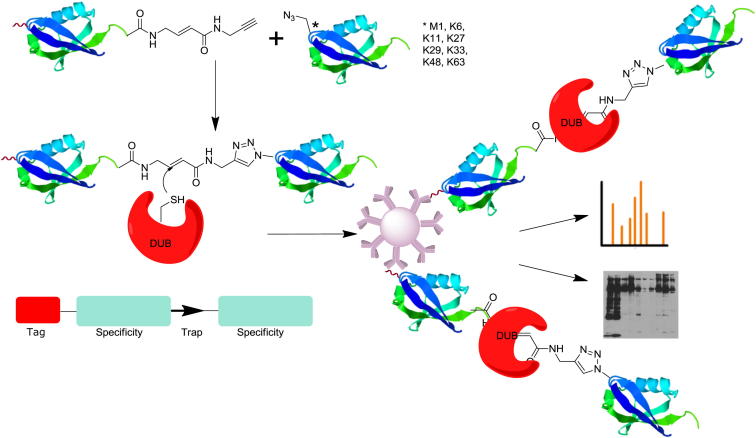
Figure 1.
Schematic Illustration of Di-Ub Probes and Applications
Di-Ub probes were designed, consisting of two linked Ub moieties representing all Ub-linkages determining the specificity for DUBs that bind to the probe. Linkage specificity is achieved by incorporating Aha at the N-terminal methionine or in the positions of lysine residues in the proximal Ub. An electrophilic moiety in the “warhead” linking the two Ub molecules allowed covalent trapping of DUBs/Ub processing enzymes with a cysteine in the active site. DUBs/Ub processing enzymes bound to the probe could be characterized by gel electrophoresis and immunoblotting or identified after an immunoprecipitation (IP) by tandem mass spectrometry (LC-MS/MS) analysis.
See also Figure S1.