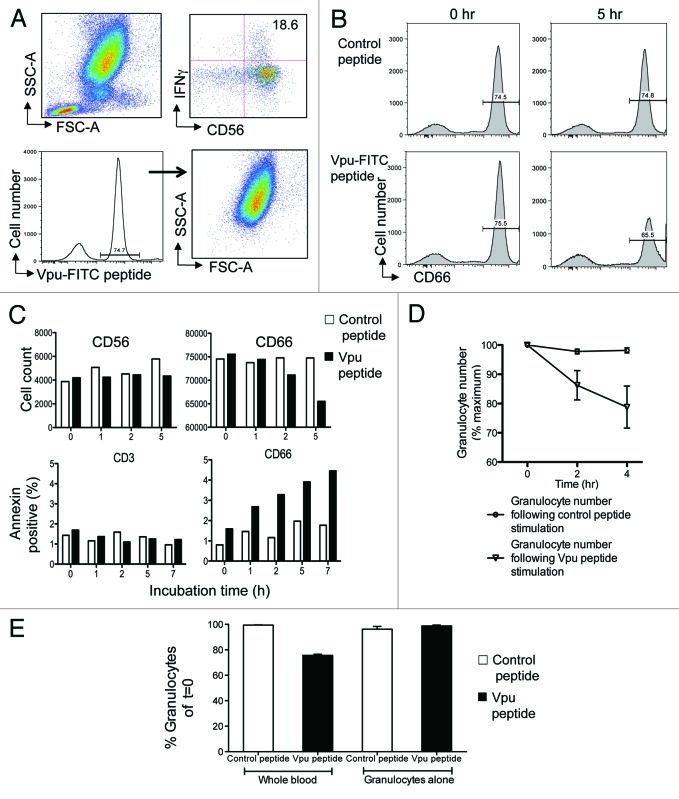
Figure 2. Granulocytes express ADCC epitopes and are targets for killing. (A) Fluorescently labeled Vpu peptide bind to granulocytes. The ADCC epitope Vpu peptide 19 (sequence EMGHHAPWDVDDL) was conjugated with FITC fluorochrome. The fluorescent Vpu peptide induced robust ADCC activity in the presence of HIV+ plasma (top right plot). Based on FSC and SCC criteria, cells expressing fluorescent peptide localized primarily to granulocytes (bottom right plot). (B) Loss of CD66c+ granulocytes (bottom right plot) occurs in the presence of HIV+ plasma during the 5 h incubation following stimulation by Vpu peptide compared with a control peptide (sequence KKFGAEVVPC) that has no known ADCC inducing ability (top right plot). (C) Granulocytes are the major cells that undergo apoptosis in the NK cell activation ADCC assay in the presence of HIV+ plasma. Decrease in CD66c+ granulocytes (top right graph) but not CD56+ NK cells (top left graph) occurred over time. Annexin V staining indicated that CD66c+ granulocytes were undergoing apoptosis (bottom right graph) compared with CD3+ T cell populations over time. Cell loss and Annexin expression in the presence of Vpu peptide (black bars) was compared with a control peptide (white bars). (D) Across 5 donors, granulocyte numbers reproducibly fell in the presence of HIV+ plasma following Vpu peptide stimulation (circles) compared with control peptide stimulation (triangles; mean and SD shown). (E) Granulocyte loss does not occur in the absence of other leukocytes. Granulocytes numbers decrease in the presence of HIV+ plasma when the ADCC assay is performed in whole blood containing NK cells (2nd bar) but not in the presence of purified granulocytes alone (4th bar). Loss of granulocytes in the presence of Vpu peptide (black bars) was compared with incubation in the presence of a control peptide (white bars).

An official website of the United States government
Here's how you know
Official websites use .gov
A
.gov website belongs to an official
government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS
A lock (
) or https:// means you've safely
connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive
information only on official, secure websites.