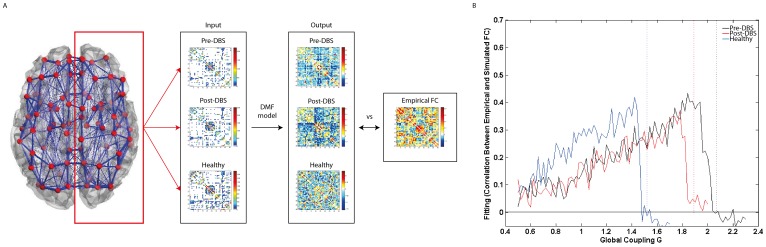
Figure 5. Exploring the impact of DBS-induced structural changes on resting-state functional connectivity.
A) Schematic overview of how the simulated FC matrices are obtained from the SC matrices using the dynamic mean field (DMF) model. The simulated FC matrices are subsequently compared to the empirical resting state FC matrix. B) Solid lines indicate the fitting of simulated functional connectivity (FC) matrices obtained with the pre-DBS (black), post-DBS (red), and healthy controls (blue) structural connectivity matrices with the empirical healthy FC, as a function of the global coupling weight (G). Vertical dashed lines indicate the corresponding bifurcation points, above which the dynamics becomes unstable. We observe that the bifurcation point of the post-DBS FC is shifted from the pre-DBS FC bifurcation point towards the healthy bifurcation point. This means that, before DBS, the structural connectivity is weaker and therefore stronger couplings are required to reach an optimal fitting with empirical FC The shift of the post-DBS bifurcation point towards the healthy bifurcation point indicates recovery of the structural connectivity with DBS.