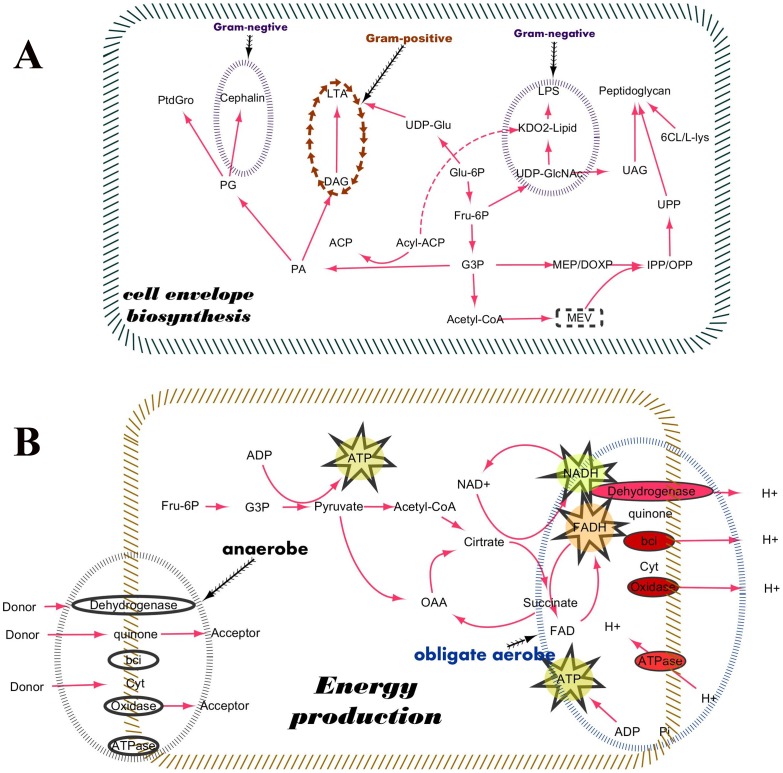
Figure 3. Difference in phenotype and lifestyle.
A) Pathway differences between Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria. These pathways include phosphoglycerolipid and glycerolipid metabolism, terpenoid backbone biosynthesis, peptidoglycan biosynthesis, and lipopolysaccharide biosynthesis. Bacteria are categorized as either Gram-negative or Gram-positive based on differences in their cell wall compositions. The greatest difference is that Gram-negative bacteria contain an outer membrane with lipopolysaccharides, whereas lipoteichoic acid is found in the outer membrane of Gram-positive bacteria. B) Pathway differences between anaerobic and aerobic bacteria. Bacteria possess an important respiratory chain for energy production and maintenance of redox balance. The electron transport chains between obligate aerobic and anaerobic bacteria contain several different electron donors and acceptors. Electrons can enter the chain at three levels: a dehydrogenase, a quinone pool, or a mobile cytochrome electron carrier, all of which correspond to successively lower Gibbs free energy changes.