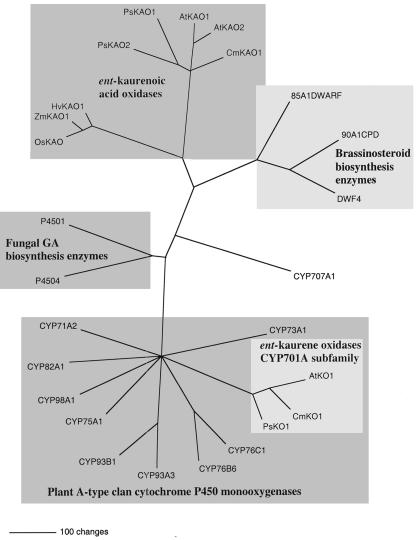
Figure 5.
Inferred phylogenetic relationship of ent-kaurene oxidases (CYP701A) and representatives of related cytochrome P450 enzymes. The unrooted phylogram was generated by PAUP 4.0b10 analysis (Swofford, 1999) using putative amino acids of full-length genes (excluding gaps). The ent-kaurene oxidase proteins used in addition to the pea PsKO1 were AtKO1(GA3; AAC39507; Helliwell et al., 1998) and CmKO1(AAG41776; Helliwell et al., 2000). A representative of the plant A-type cytochrome P450 clan subfamilies CYP75A, 93A, 93B, 76B, 76C, 82A, 73A, 98A, and 71A were included. GA biosynthesis kaurenoic acid oxidase proteins used in addition to the pea PsKAO1 and PsKAO2 were from Arabidopsis (AtKAO1 and AtKAO2), pumpkin (CmKAO1), rice (OsKAO1), maize (Zea mays; D3: ZmKAO1), and barley (Hordeum vulgare; Grd5: HvKAO1). The related brassinosteroid biosynthetic enzymes used include Arabidopsis CPD (CYP90A1), brassinosteroid-6-oxidase and DWF4 (CYP90B1), and tomato (Lycopersicon esculentum) DWARF (CYP85A1). The fungal P450–1 and P450–4 GA biosynthesis enzymes with ent-kaurene oxidase and ent-kaurenoic acid oxidase activity were also included.